A horse with a club foot is kind of like a horse in high heels The hoof angle becomes raised and the horse walks on his toe due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit (the unit includingFetlock is a term used for the joint where the cannon bone, the proximal sesamoid bones, and the first phalanx (long pastern bone) meet The pastern is the area between the hoof and the fetlock joint Disorders of the fetlock and pastern include conditions such as fractures, osteoarthritis, osselets, ringbone, sesamoiditis, synovitis, andClub Feet With the Club Foot, one foot is steeper than the other It wants to, needs to, etc but it is not a hoof problem The horse is adapting to something else Go on a detective mission There is/was an injury, nerve damage, or opposite hind stifle problem as examples Massage folks can really help the club foot horse

Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals
Club foot horse pictures
Club foot horse pictures-Once a horse reaches twoyearsold with a club foot or high/low conformation, it is very likely that it will remain, to some degree, for the rest of the horse's life no matter what you do By then, the joint surfaces, bone shapes, muscles, tendon and ligament lengths have• rotatory subluxation of talocalnoenavicular joint (subtalar) complex with talus in plantar flexion and subtalar complex in medial rotation and inversion • also reffered as clubfoot • talipes derived from term talus ankle & pes foot • equinovarus derived from word equino like a horse & varus turned inward 4




The Importance Of Physical Maturity In The Horse Horsetalk Co Nz
The foot appears to be sideways or sometimes even upsidedown The foot may be smaller than a normal foot by up to a halfinch The calf muscles on the affected leg may not be fully developedSoCalled Club Foot in Horses by James R Rooney, DMV Published in the October 1999 Issue of Anvil Magazine Fig 1 Drawings by Lungwitz (1910) Socalled "clubfoot" has long been a vexing problem for horsemen, veterinarians, and farriers The term clubfoot is a misnomer for the condition in the horse and correctly refers only to a Club foot is one of the most common deformities in the horse world Horses affected with club foot develop a flexural deformity of the coffin joint, due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit that starts high up in the limb and inserts on the coffin bone in the foot, resulting in an upright conformation of the foot
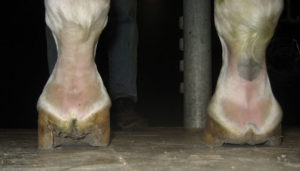
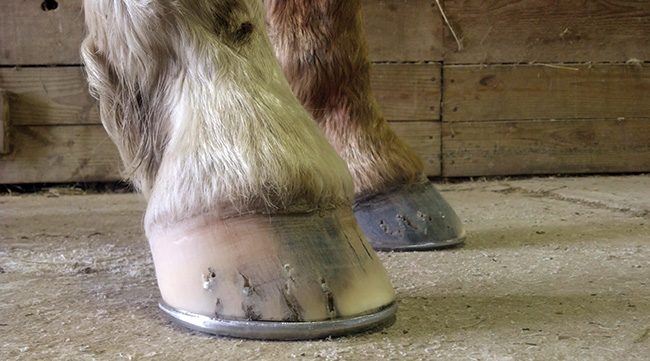
club foot case recently This particular horse, a six year old gelding, has what I feel is a grade three club foot (on a 15 scale) Apparently the club foot condition has been with this horse since it was a foal This horse found it difficult toThe front legs bear about 60 percent of the weight of a horse Healthy horses stand at rest with weight equally distributed on both front legs Lameness in the foot or leg will cause "pointing" Pointing refers to a state of rest with one foot positioned about 10 to 12 inches ahead of the other in an effort to reduce weight on the affected side A horse with slightly asymmetrical feet is nothing out of the ordinary But if one hoof differs dramatically from the other, you might be dealing with a
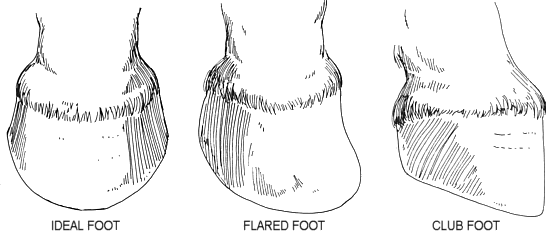
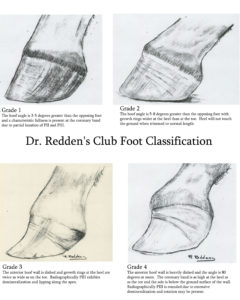
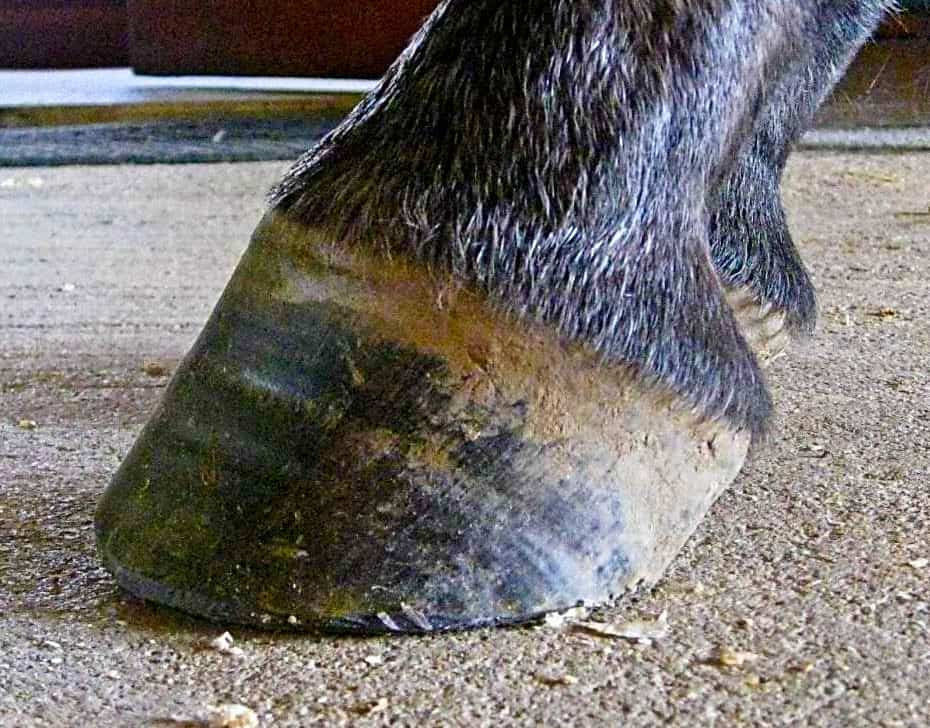
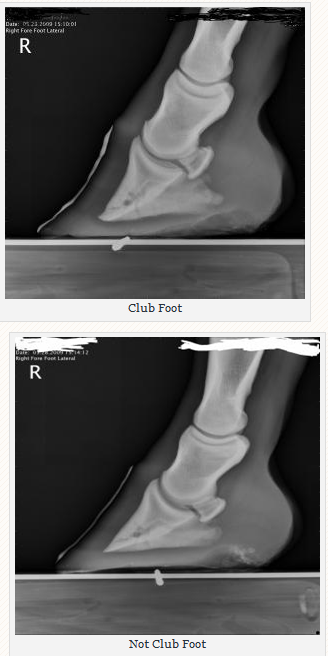
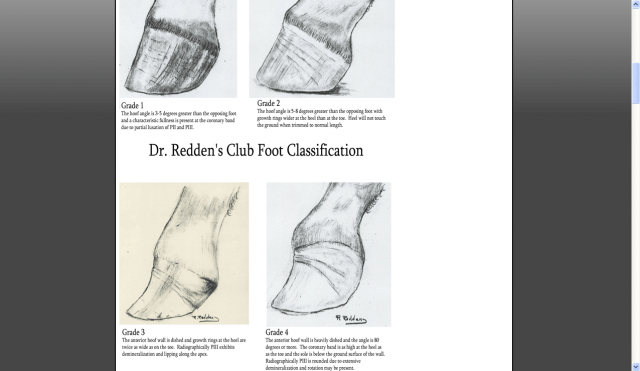
In the horse, hoof growth is dictated in large part by weight distribution If a horse puts more weight on the inside of a hoof, the blood is pushed to the opposite side of the foot causing faster growth and wearing down the weighted surface at a faster rate With respect to the club foot, the heel of the affected foot grows faster and the hoofAnklefoot orthoses (AFO's), is a hard rigid molded plastic splint held on with velcro worn on the lower leg and foot to support the ankle, hold the foot and ankle in the correct position, and correct footdrop This type of AFO was used for clubfoot surgical treatment methods and is not part of the Ponseti Method A horse with an upright alignment of the pastern bones will also have upright hoovesa situation that is sometimes mistaken for club foot A true club foot is significantly more upright than the other hooves, or the angles of both hoof walls are steeper than the angles of the pasterns The severity of the problem is commonly graded on a four



2



What Causes Club Feet American Farriers Journal
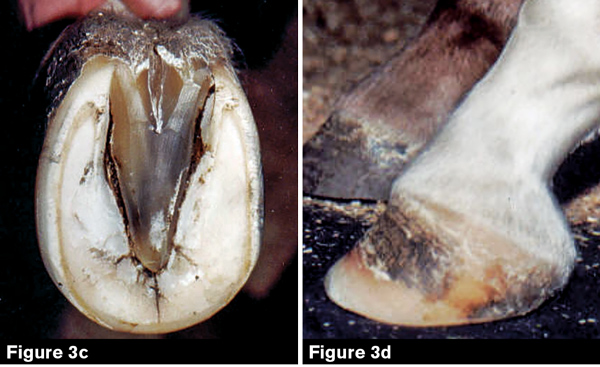
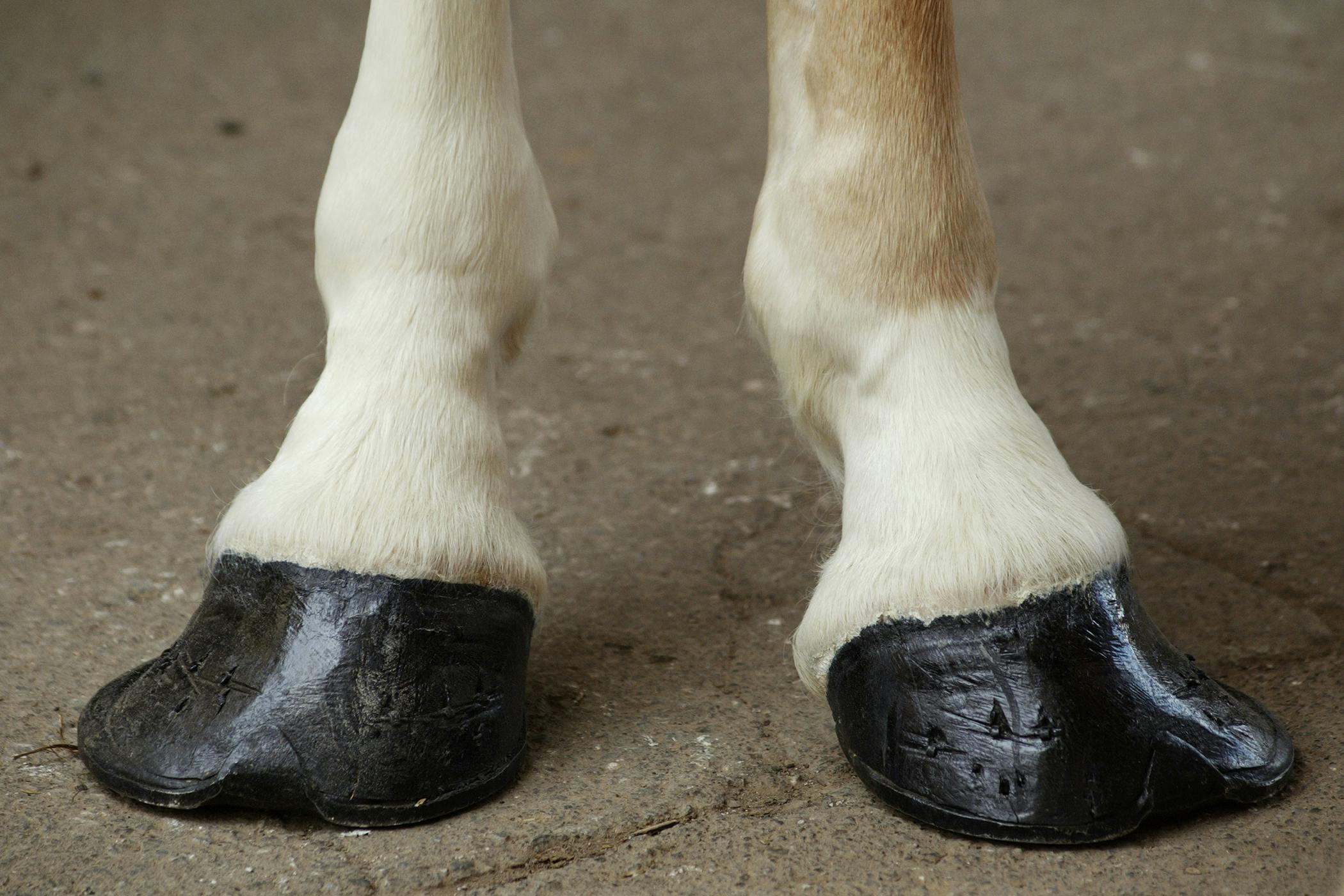
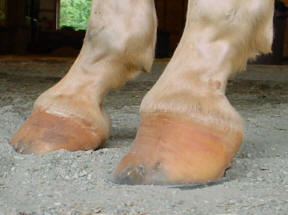
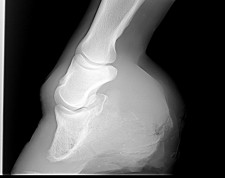
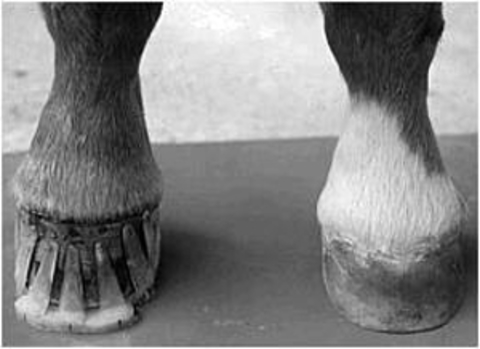
The club foot can range from those that are barely noticeable to the extreme of the foot pointing backwards But the barely noticeable club foot may come out in a later generation as an extreme club foot It is also totally unfair to blame the farrier for the club footContracted heels in horses sometimes are mistakenly called club foot These are in fact two different conditions but have a lot in common and the result is similar Cases of contracted heel can be primary or secondary In primary cases, contracted heel is a result of unbalanced feet or overgrown hoofsOf club foot A horse with club foot has one hoof that grows more upright than the other The "up" foot is accompanied by a broken forward pastern, that is, the hoof is steeper than the pastern (Photo 1) In a normal foot, the hoof capsule and the pastern align Radiographs will




Pdf Management Of Clubfoot In Horses Foals To Adults Semantic Scholar




Pdf The Incidence Of Acquired Flexural Deformity And Unilateral Club Foot Uneven Feet In Thoroughbred Foals
Pain can arise from physitis, osteochondrosis, degenerative joint disease, pedal bone fracture, or softtissue wounds and infection Pain induces reflex muscle contraction with shortening of the flexor musculotendinous units The horse walks on its toes or knuckles in the fetlocks or occasionally the pastern jointThree Bars, the most influential Thoroughbred in American Quarter Horse history, was foaled near Lexington Despite severe circulatory problems in a hind leg, Three Bars won races as a three, four, and fiveyearold As a sixyearold in 1946, he set a 57 3/5 track record over five furlongs at the Phoenix Fairgrounds in ArizonaThis is the first of many pages displaying horse hoof anatomy pictures My goal is to begin with the basic external parts of the hoof and progress to the internal workings of the foot I want to help you visualize everything in the horse's hoof, understand the relationship between the parts and learn to read the clues the hooves have to offer



Club Foot




Club Foot Results In A Vertical Hoof Wall Compared To Other Feet A Dropped Sole And A Dished Front Dorsal Hoof Wall It Res Club Foot Horse Health Hoof Care
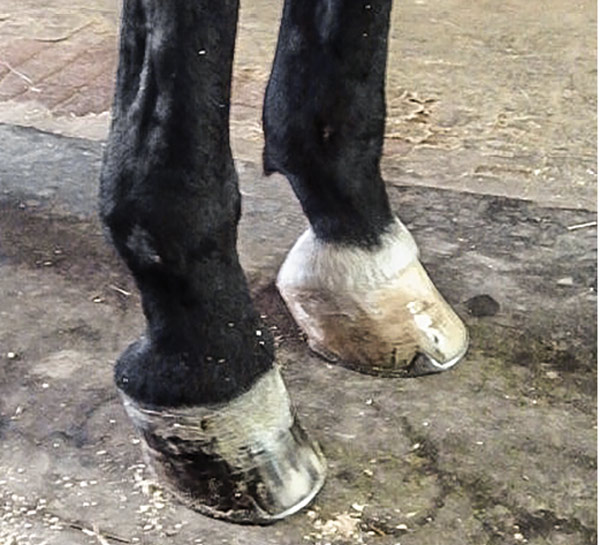
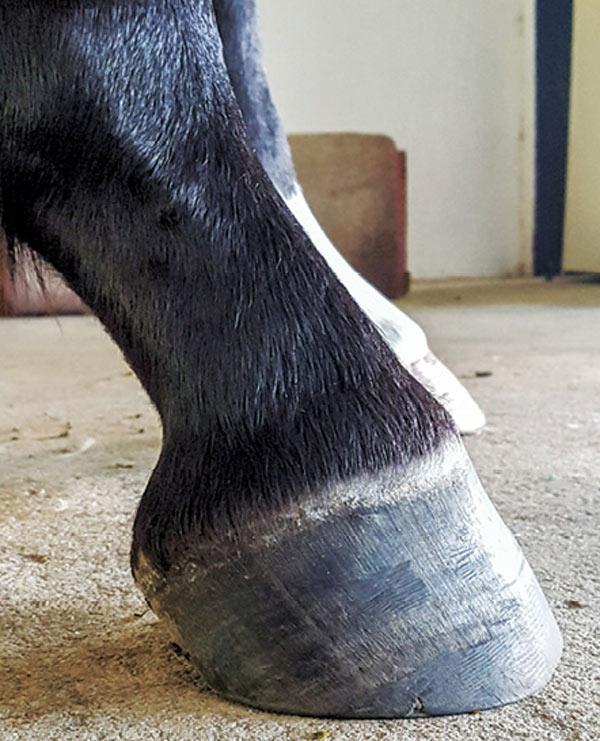
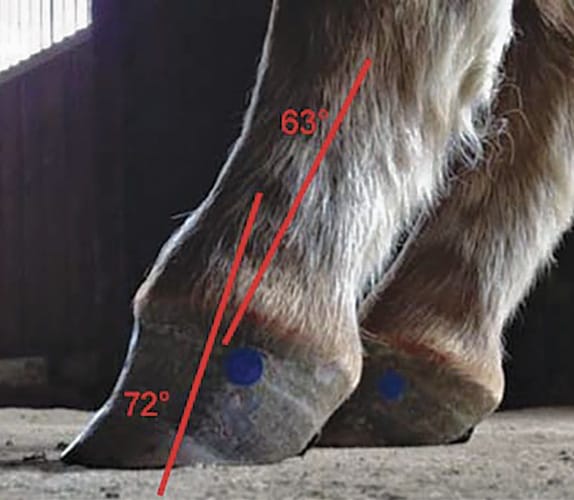
There are four grades of club foot Grades 1 to 4 as follows Grade 1 – Only note a difference in the hoof angles that returns with each trim Grade 2 – Greater difference in hoof angles, growth rings begin to change There is an air gap (space between the bottom of the heel and the ground bearing surface heel does not fully weight bear/load on the groundThe xray will show whether the hoof pastern axis is parallel If the axis is broken forward (club foot) or if the axis is broken back (long toe underrun heel), the radiograph will reveal the degree of deformity and the best way to trim the foot to improve it Using landmarks, measurements can be drawn on the radiographs and transferred to theClub Foot This is a pacer with a right front foot that is clubfooted It has a high degree of hoof wall to postern axis angle of approximately 60 degrees I believe this was congenital rather than injury related He was shod with a wide web, set back shoe Trimming and shoe placement was the key to longterm soundness for this horse



Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals
About me Whole Horse Trimming and Certification Program My name is Ida Hammer I am a Whole Horse trimmer, Rehabilitation specialist, Hoof trim educator and consultant I have been around horses, pretty much my whole life I have ridden competitive trail rides, jockeyed race horses, barrel raced, did a little cutting, and relaxing trail ridesAny club foot that has been around a while will have a sensitive, unused, underdeveloped frog/digital cushion You can fix everything else and still have the back of the foot too sensitive for the horse to land on, which will cause the shortened stride and resulting club foot on its own – another vicious cycleEquine Club Foot The equine club foot is defined as a hoof angle greater than 60 degrees What we see externally as the equine clubbed foot is actually caused by a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint (coffin joint) Causes include nutritional issues, heredity, position in the uterus or




Ballerina Syndrome Where The Heels Remain Off The Ground Even At The Download Scientific Diagram



Animal Mrt Effect Of Hoof Distortion On Muscoskeletal Issues
Example of a club foot The term "clubfoot" gets thrown around a lot when describing the way a horse, particularly a sale prospect, looks EquiSport Photos (Matt and Wendy Wooley) Eric KaletExplore Kayla Reynolds's board "Club Foot" on See more ideas about club foot, horse health, horse careSymptoms of Club Foot in Horses Lameness Pain Excess toe wear Shortening of the tendon that is attached to the coffin bone Impacts the standing or movement of your young horse It can affect one or both limbs usually in the fore limbs Coronary band may bulge as the deformity progresses



Horse Hoof Irregularities Club Foot Integrity Horse Feed



Horse Hoof Irregularities Club Foot Integrity Horse Feed
Club feet are surprisingly common, with up to 60% of the domestic horse population exhibiting at least minor characteristics Several theories address the potential causes, ranging from a genetic predisposition, to hoof or body injury, to improper trimming and/or shoeingFor more information on studies of the Australian Bumbry refer to Chapter 2, The Feral Horse Foot The Australian Brumby Studies, Brian Hampson, PhD, in the new book by Pete Ramey, Care and Rehabilitation of the Equine Foot, 11 Environment is obviously important in shaping the foot but genetics must also play a role Club Foot Conformation in Horses Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon, a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoof's biomechanics Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle, a distended coronary band, growth rings that are wider at the heels



Welcome Princess 17 Page 2 Zenyatta Com Forums




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome
Common Horse Hoof Problems "No hoof, no horse" It's such a simple statement, but it holds so much truth Your horse's hooves provide the foundation for everything you two do together, so it's important to know the horse hoof care that will keep them healthy and sound But sometimes that's easier said than doneIn the donkey's foot, the bulbs of the heel are much more pronounced than that of a horse, and this is why the donkey frog is set back much further than the point of balance of the horses foot The donkey relies on this bulb, (almost like a camel's foot) to act as a traction device, or a cushioning device for hard terrainRelated Images wildlife animals stallion mammal We handpicked the best horse images for your choosing Ready for commercial use, all in HD to 4K quality 1251 1217 132 girl daydreaming horse 1147 1105 123 white horse winter snow white horse on white sand 859 816 130



Is This A Club Foot Horsetalk Co Nz




A Club Foot Is Caused By Mobile Equine Diagnostics Inc Facebook
Even horses born with a club foot have no reason to maintain the damage If the bone shape underneath is correct the hoof will grow correctly Some how I think we have diverted from the origonal topic of odd stances Even though a club foot is a common cause of odd stances, pain in parts of the hoof can also drive the problem 4 Schedule regular farrier visits according to your horse's individual needs Although six to eight weeks is the average, there's really no standard interval for trimming and shoeing If your farrier is correcting for a problem such as underrun heels, a club foot, or flare in the hoof wall, your horse may benefit from a shorter intervalAdult club foot requires a completely different approach to treatment than juvenile club foot In many cases, mild club foot is not associated with lameness or decreased performance Many great performance horses have managed to perform well with a club foot However, there is a greater likelihood of lameness occurring in club feet than in
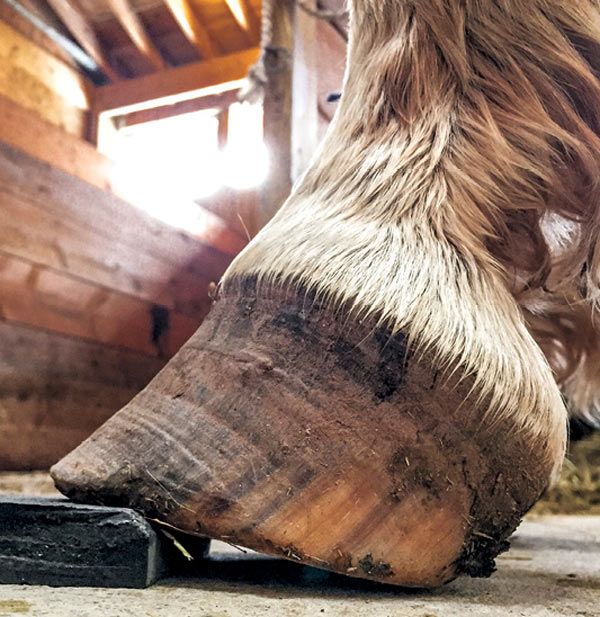




Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource
Casting for Club Foot Using the Ponseti method, the clubfoot is manipulated or stretched every five to seven days and the plaster casts are changedThis baby is on one of his last treatments for his clubfeet and will then wear a brace for a few years An alternative to serial casting is a specialized physical therapy treatment program, in which your child undergoes dailyHorses with obvious club feet land more on the toes, causing toe bruising or laminitis The horse will generally do poorly at prolonged exercise, especially on hard or uneven terrain (eventing, trail riding) Because the toe is easily bruised, the horse will move with a "Club feet can also be due to a pain response Often the club foot or feet are secondary to OCD lesions in the shoulder, for instance," says Burns If it's painful for the horse to put weight on that limb, or favors it a little bit, the flexor muscles eventually contract and pull the heel up, with the horse walking more on the toe




The Barefoot Horse Magazine What S The Problem With A Club Foot Can You Or Should You Try Fix A Club Foot By Trimming Shoeing Can A Horse With A Club



Club Foot In Horses Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost
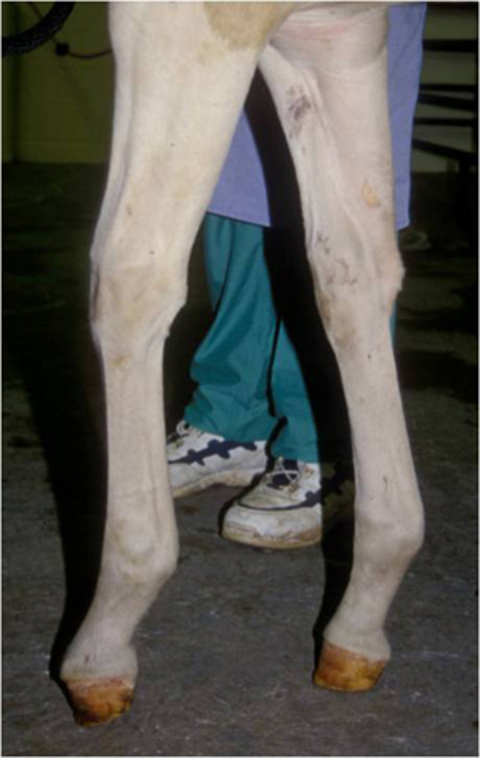
Clubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward The affected foot and leg may be smaller than the other Approximately 50% of cases of clubfoot affect both feet Most of the time, it is not associated with other problems Without treatment, the foot remains deformed, and people walk on the sides of their feet This may lead to pain and difficulty walking High/Low Syndrome This horse exhibits what is sometimes called "high/low syndrome" with one foot having high heels usually on a contracted foot (which may or may not be a clubfoot), and the other with low and sometimes underrun heels, flat and lacking concavity The horse usually stands in a scissor stance, with the highheeled foot back behind Clubfoot can be repaired by casting or surgery Casting Sometimes nonsurgical treatments, such as casting, can correct clubfoot Casting is a




Club Foot Or Not Barefoot Hoofcare




Hoof Conformation Vs Horse Conformation Scoot Boots Retail



The Tolerable Club Foot The Horse




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Frequent Trips Aid Club Foot American Farriers Journal




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith




How D That Happen Origins And Remedies For Clubfoot Horse Racing News Paulick Report




Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot American Farriers Journal




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



1



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource




Hoof Conformation Vs Horse Conformation Scoot Boots Retail



Club Foot Chronically Unsound Barefoot Hoofcare




Is This A Club Foot Horsetalk Co Nz




The Importance Of Physical Maturity In The Horse Horsetalk Co Nz




Horseadvice Com Equine Horse Advice 22 Months Old With A Club Foot




Club Foot Just How Sore Is Your Horse Casey Son Horseshoeing School




Why Some Horses Develop A Clubbed Foot Holistichorse Com




Equine Club Foot



Lesson 4



Would You Buy A Horse With Club Foot Pics The Horse Forum



Hoof Care Email Q A American Farriers Journal
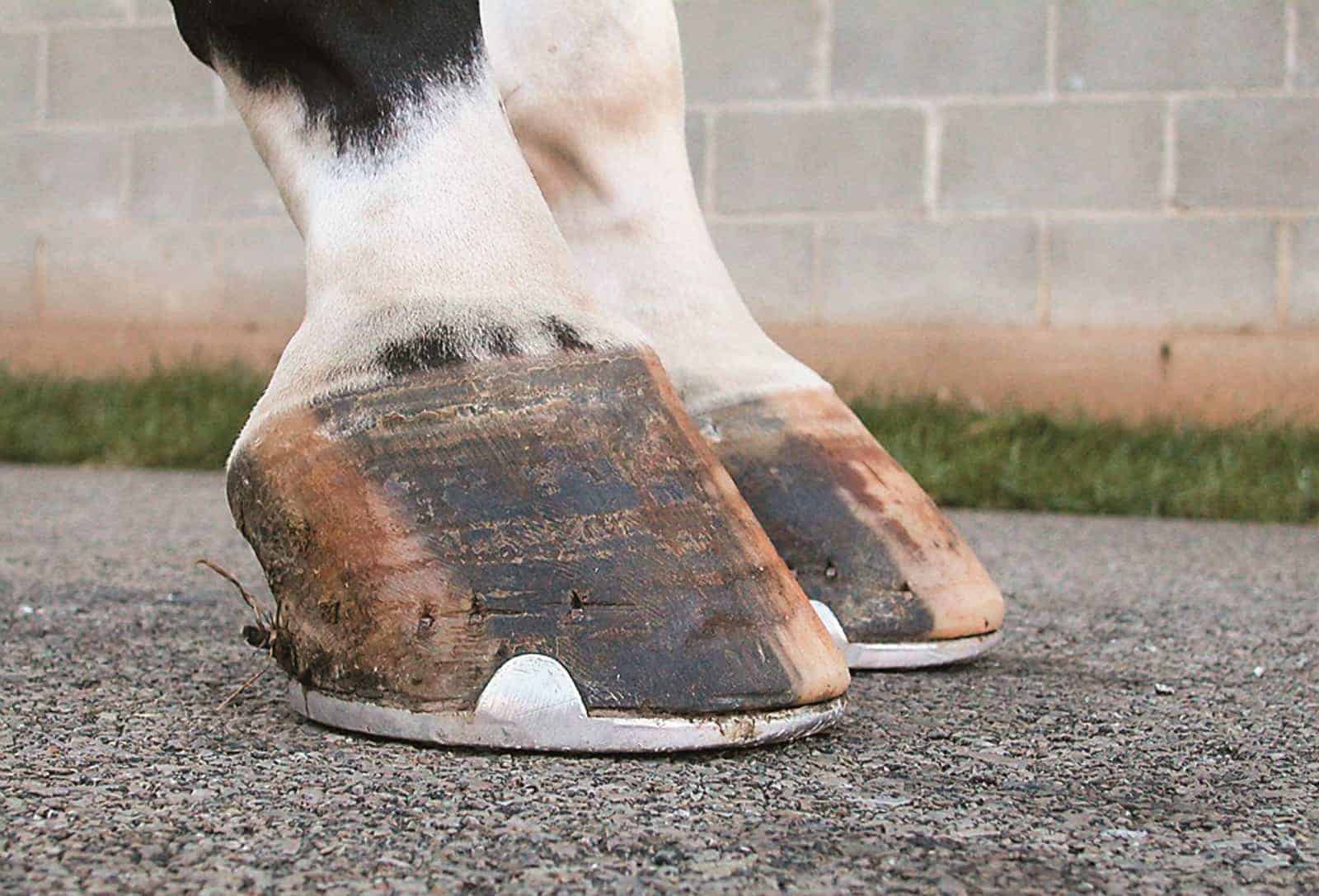




Managing The Club Foot The Horse




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith



What Advice Has Been Most Helpful When You First Encounter A Club Foot American Farriers Journal



2




What Is A Club Hoof Versatile Horsemanship Youtube
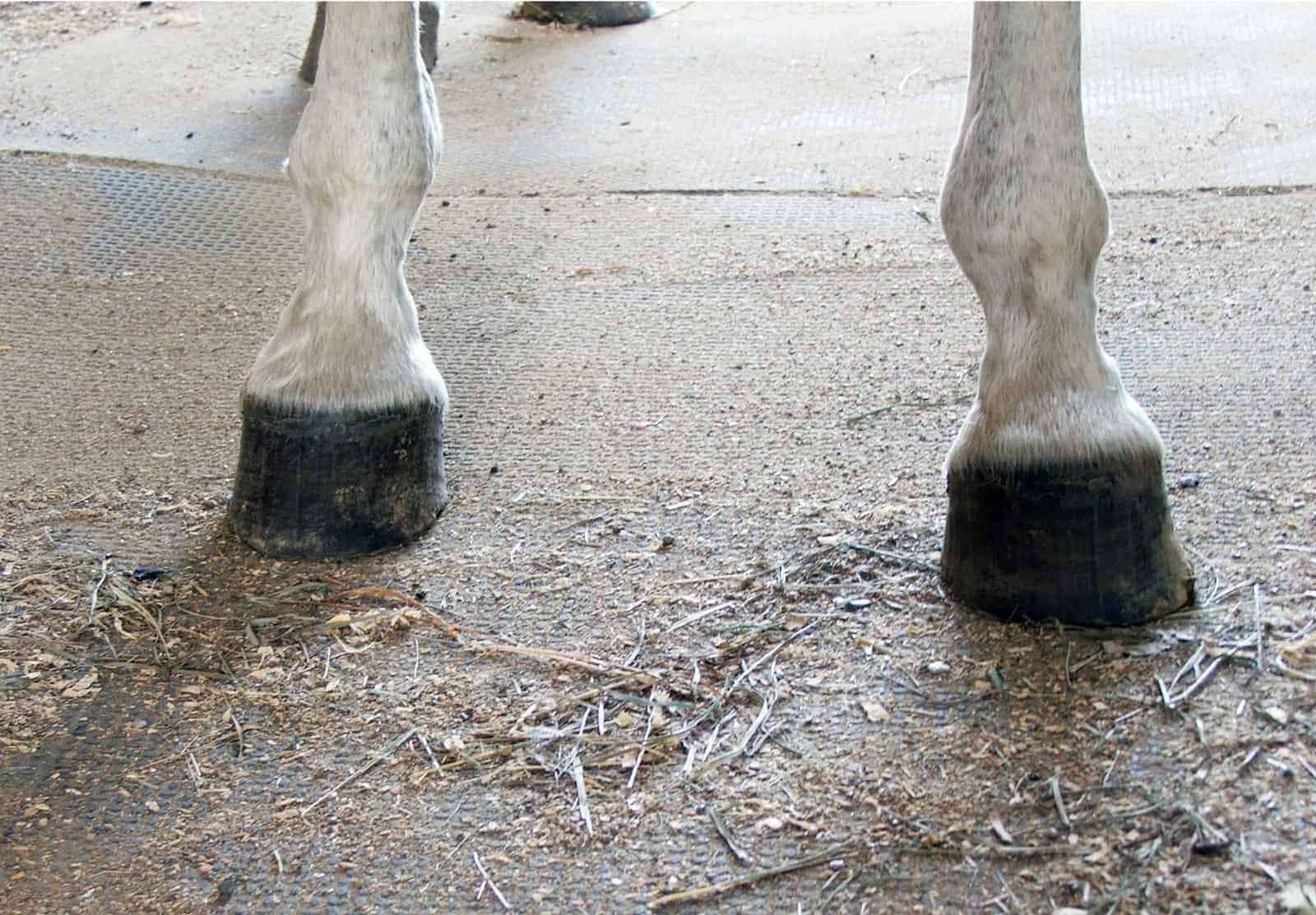




Club Foot Heritability In Horses The Horse



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog



Club Foot



Club Foot In Horses



Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo



1



Farriervet Lancaster Club Foot



Would You Buy A Horse With Club Foot Pics The Horse Forum




Club Foot What Does The Future Hold For Your Foal H H Vip Horse Hound




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Horse Foot




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




News Feed Casey Son Horseshoeing School




Webinar Shoeing The Club Footed Horse Youtube




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Club Feet In Foals



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News




The Club Foot Is It No Big Deal Or A Deal Breaker




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource



Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome




Club Foot In Horses Brian S Burks Fox Run Equine Center Facebook



Club Foot



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News



Club Feet Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



Equine Podiatry Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Is This A Club Foot Horsetalk Co Nz



Clubfoot 5 Yo Morgan Mare Barefoot Hoofcare




Pdf Management Of Clubfoot In Horses Foals To Adults Semantic Scholar



So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv



Equine Club Foot



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo



Club Feet In Foals




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot American Farriers Journal
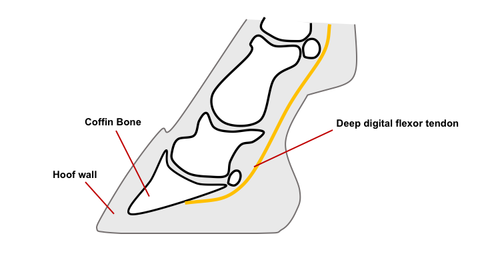



Club Feet In Foals



Shoeing News Club Grades Harness Racing Newsroom Usta Ustrotting



Club Foot
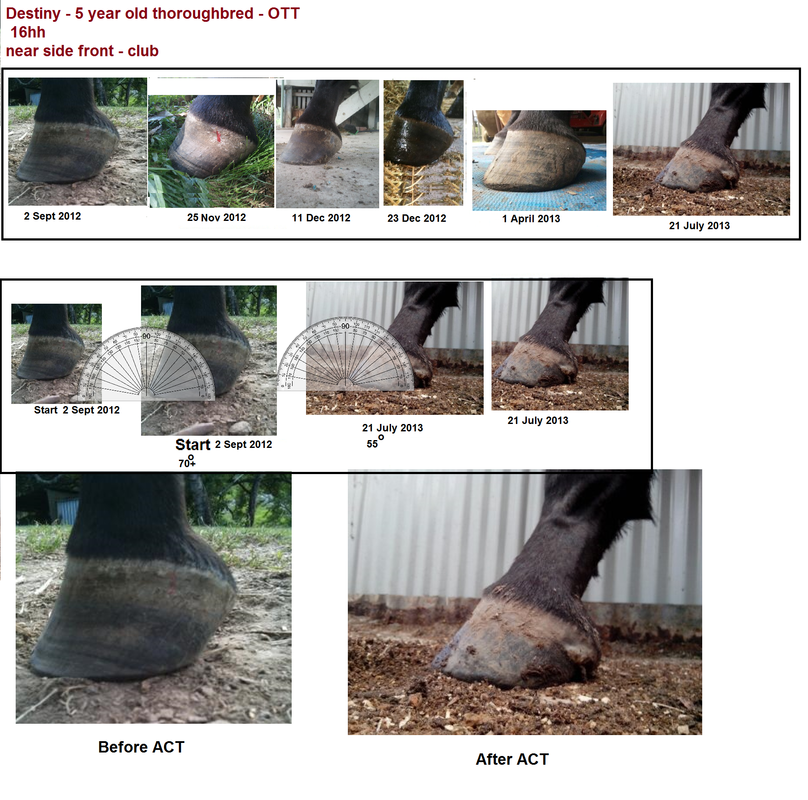



Club Foot Rehabilitation Act Trimming Strategy
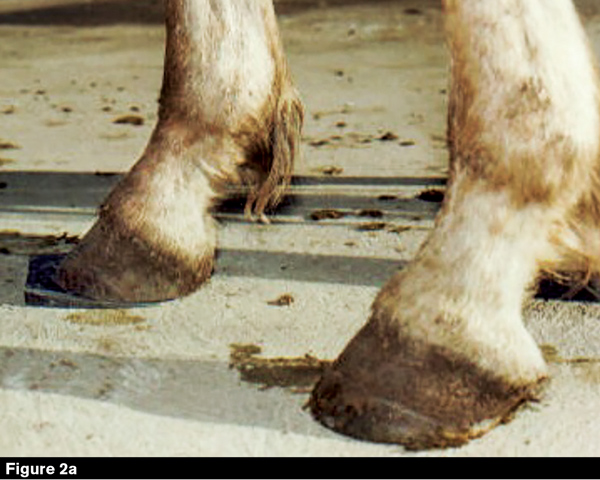




What Causes Club Feet American Farriers Journal



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles
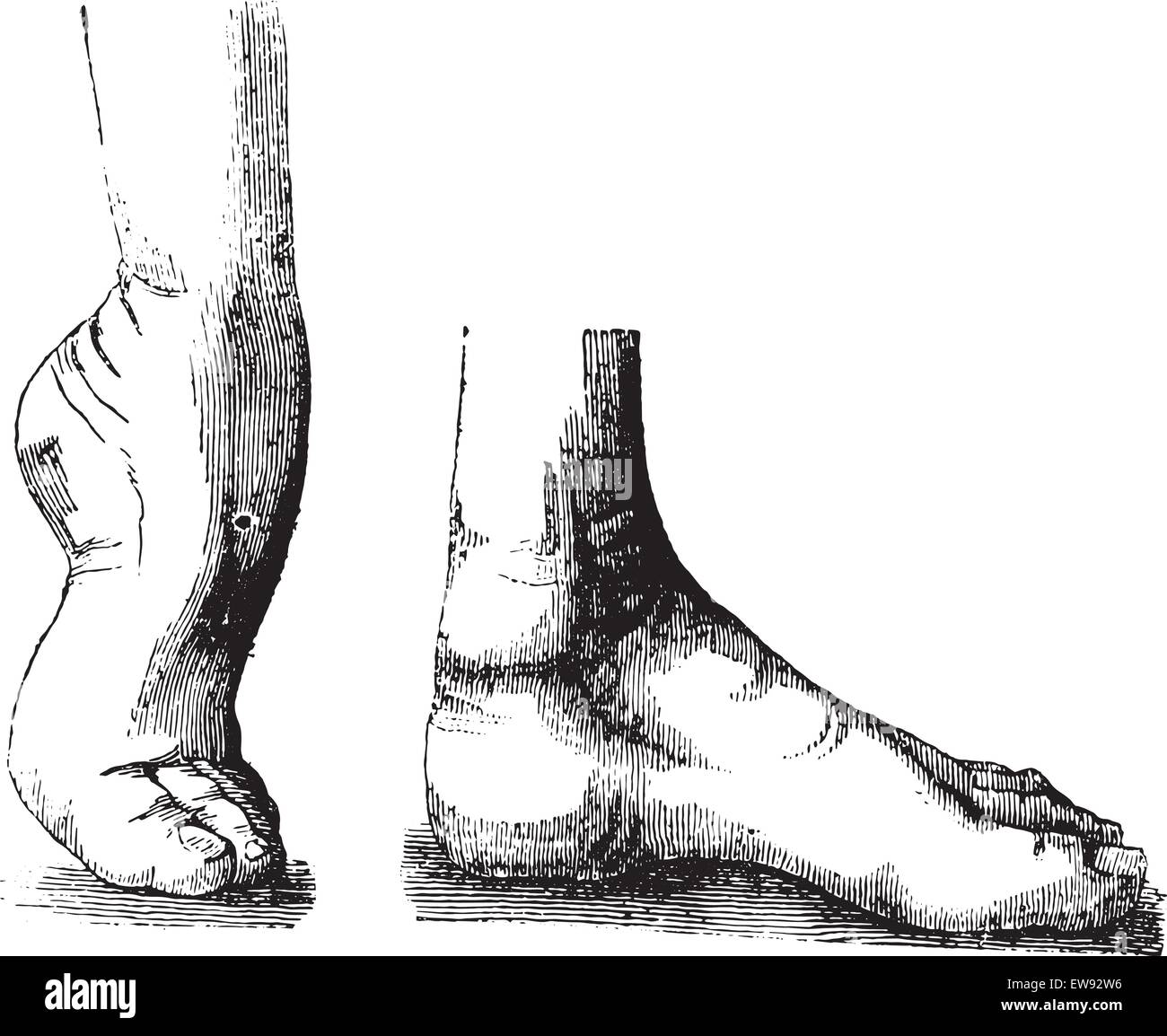



Club Foot High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



1




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses




What Causes Club Feet American Farriers Journal




Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles




28 Club Foot Ideas Club Foot Horse Health Horse Care




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome




Club Foot Ronaldmarshall




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿