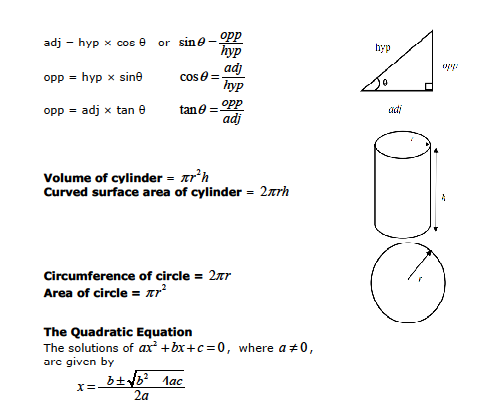
A lot of the formulas for maths GCSE are common sense I find You are given (p = pi and rr is r squared) Area of Trapezium = 1/2 (ab)h Volume of Prism = area of cross section x length Volume of Sphere = 4/3prrr Surface area of sphere = 4prr Voluke ofMaths Olympiad participants, how did you start getting good?I want to help you achieve the grades you (and I) know you are capable of;
Http Www St Anthonys Academy Com Wp Content Uploads 14 07 Gcse Formulae Sheet Foundation Pdf
Equations needed for gcse maths
Equations needed for gcse maths-Simultaneous equations are a key part of algebra for GCSE maths To do well with simultaneous equations you need to be confident solving difficult linear equations Check out our linear equations guide and worksheet if you need to revise this before going any further Once you're confident with linear equations read on and find out how toUsing words or letters Example 1 Cost of hiring a van = number of days × £40 £100 This formula allows you to calculate the cost of hiring a van based on the number of days it is needed for
/Quadratic-Equations-(H).jpg)



Gcse Quadratic Equations Solving Unknown Quantities
The equation of a circle Any point P with coordinates \((x, y)\) on the circumference of a circle can be joined to the centre (0, 0) by a straight line that forms the hypotenuse of a right angleOne linear equation and one quadratic equation y = x 3 y = x2 5x −2 y = x 3 y = x 2 5 x − 2• 23 equations students need to know and be able to apply (21 in Combined Science) • 12 equations students must be able to select and apply (7 in Combined Science) • Grades 13 will be given equations to apply Simple equations with substitution of two numbers, no transformations
Cos ( A) = b 2 c 2 − a 2 2 b c \cos (\textcolor {limegreen} {A}) = \dfrac {\textcolor {blue} {b}^2\textcolor {blue} {c}^2 \textcolor {limegreen} {a}^2} {2\textcolor {blue} {b}\textcolor {red} {c}} cos(A) = 2bcb2 c2 −a2 Area of a triangle 1 2 a b sin ( C) \dfrac {1} {2}ab\sin 21Maths GCSE Top Topics tutored At MyTutor , we've got lots of dedicated Maths tutors across the UK who love helping teens achieve their best when exams come around Since we started in 13, we've given more than 250,000 onetoone lessons , and over 1 million school pupils have used our online resource centreQuadratic simultaneous equations are two or more equations that share variables that are raised to powers up to 2 eg x 2 and y 2 Below are examples of quadratic simultaneous equations that are made up of a pair of equations;
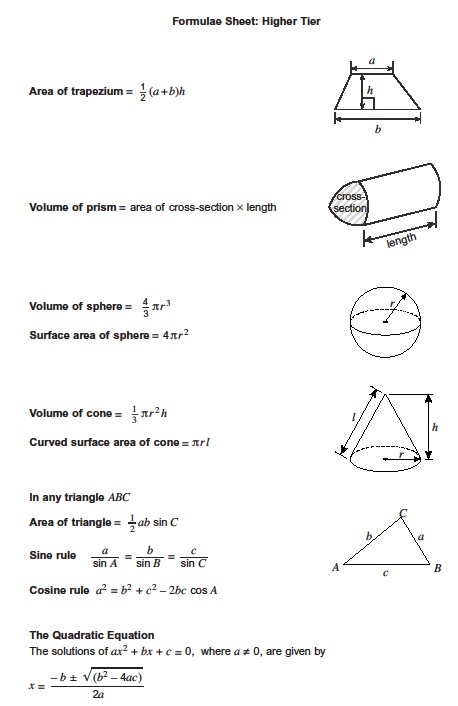
Edexcel GCSE (91) Maths needtoknow formulae wwwedexcelcom/gcsemathsformulae Pythagoras For a rightangled triangle, a2 b2 = c2 sin xo = , cos xo = , tan xo = Quadratic equations The solutions of ax2 bx c = 0, where a ≠ 0, are given by x = Circles Circumference = C π × diameter, C = πd Circumference = 2 × π × radius, C = 2πr= sin ;This bundle covers all higher tier equations needed for gcse Maths and also topic checklists when revising for exams Courses, modules, and textbooks for your search Press Enter to view all search results () Press Enter
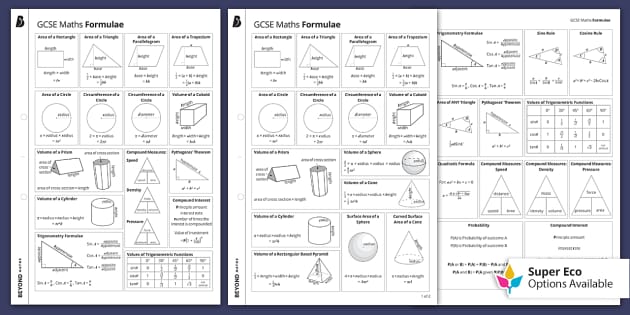



Gcse Maths Formula Sheets Overview Ks4 Maths Beyond




Pass Your Gcse Maths Equations And Graphs Tara Book Co
Sin, Cos, Tan SOHCAHTOA Rule 1 Sine is Opposite over Hypotenuse Rule 2 Cos is Adjacent over Hypotenuse Rule 3 Tan is Opposite over Adjacent Pythagoras Rule The square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides or, a2 b2 = c2 Area Square Area = Length2 Rectangle Area = Length x Width Rightangled Triangle Area = ½ x Base x Height Quadratic equations The Quadratic Equation The solutions of ax2 bX c = 0, Sine Rule sin A Cosine Rule a2 sin B sin C — b2 c2 2bc cosA Area of triangle — ab sin C 0, given MIX From responsible sources ESC FSCE C recycle finished with this please it 2a Foundation tier formulae ridam) Årtwqrk*k , Ocean jrnagèO 123RF The IGCSE mathematics formula sheet contains all the important formulas and equations from the IGCSE mathematics syllabus and which are used commonly in O level mathematics exam While solving question the formula sheet makes it easier for students to practice, they have all the formulas at one place and do not need to look for the formulas from




Gcse Maths Formulae Practice Worksheet Foundation Teaching Resources
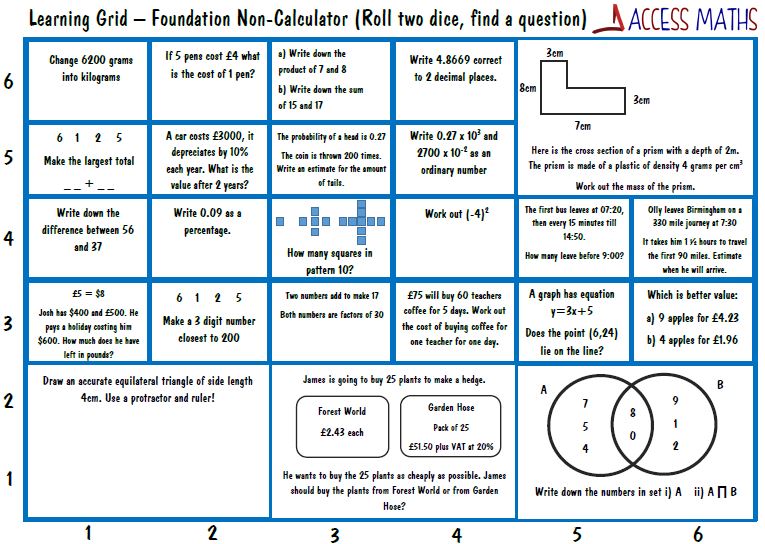



Revision Resources Access Maths
Learn how to form, solve, and rearrange equations using the tools and conventions of algebra with BBC Bitesize GCSE MathsAn area that trips a lot of students up during their GCSE maths course is quotient equations this can more easily be expressed as just "an equation with a division operation in it" Here's something you need to remember A quotient (ie a fraction) is zero only if the numerator (top half of the fraction) is zero, and the denominator (bottom half of the fraction) is not zeroIn order to factor a quadratic algebraic equation we need to make sure it is in the form of the general quadratic equation \ax^{2}bxc=0\ We must ensure the quadratic equation is equal to 0 , rearranging it if necessary
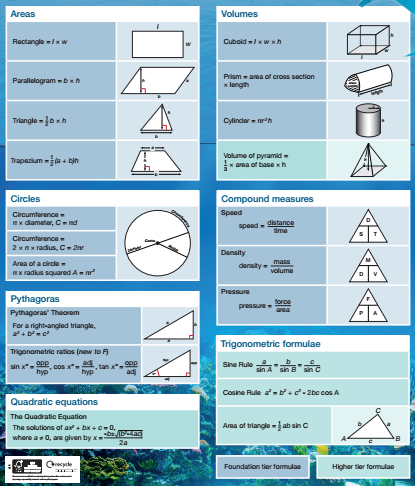



Gcse Maths Revision King Edward Vi School




Resourceaholic Five Things You Might Not Know About The New Gcse Content 2
Simultaneous Equations Here is everything you need to know about simultaneous equations for GCSE maths (Edexcel, AQA and OCR) You'll learn what simultaneous equations are and how to solve them algebraically We will also discuss their relationship to graphs and how they can be solved graphicallyEquation number Description Equation;GCSE 'Success' in Physics?




How To Remember Equations And Formulae For Gcse Maths By Phil Chambers



1
Maths Made Easy © Complete Tuition Ltd 18 Trigonometric ratios sin ;= ℎ cos ;= ℎ tan ;= The Sine rule sin ; An enlarged version of the new Formula "needtoknow" sheet from Edexcel This can be printed onto or A3 for display in your classroom This has been adapted from a Pearson resource and I am not claiming it as my own work= sin ;




Gcse Maths Symbols Equations Formulae Flashcards
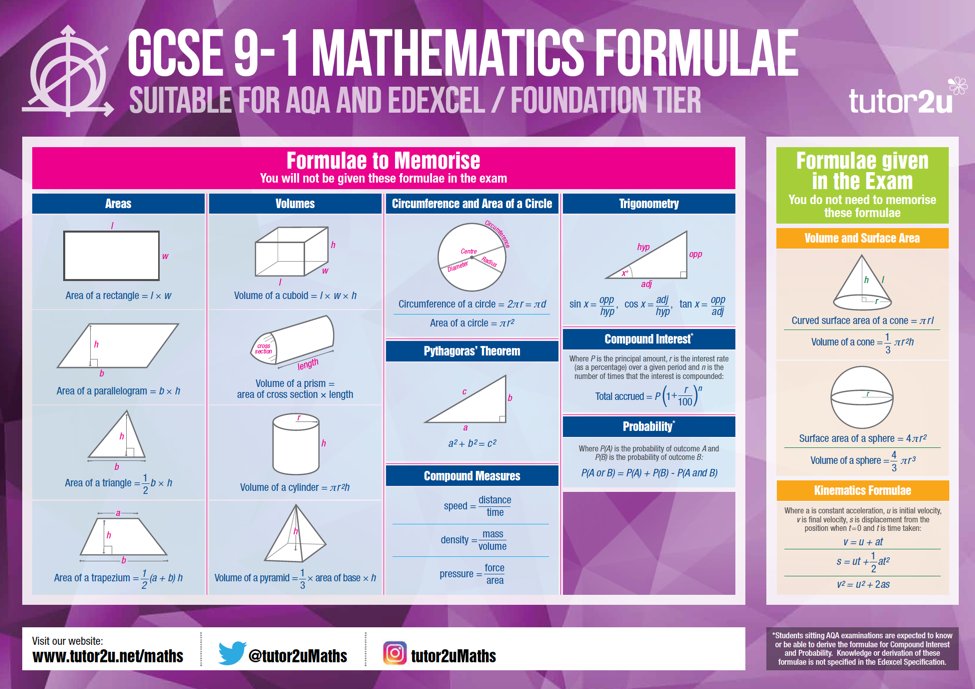



Tutor2u Maths Grab Your Free Classroom Posters On The Formulae Needed For Gcse 9 1 This Summer T Co Xwcoormtht Gcsemaths Mathsteacher T Co Yy0ndrkkxi
Appendix mathematical formulae 1 Students are expected to know the following formulae included in the subject content;They will not be given in the exam Refer to the Subject content section to determine the tier at which these formulae could be usedI need help solving equations AS Biology,Chemistry,Maths and Further Maths Maths GCSE 19 Help!




Gcse Maths Forming Formulae And Equations Anyone Know How To Do This Thanks Homeworkhelp




Gcse Maths Factorising Quadratic Equations How Would You Go About Solving These Any Links To Videos Would Be Helpful Homeworkhelp
GCSE Maths Symbols, Equations & Formulae Flashcards Info Ratings Comments Flashcards by Andrea Leyden, created more than 1 year ago This Flashcard deck shows you the formulae needed for your GCSE Maths exam This includes Algebra equations andParametric Equations So far we have seen graphs from Cartesian equations – this is where a single equation that links x and y defines a graph Sometimes, for graphs that are more complicated, it is easier to have two equations, one for x and one for y, that are linked by a shared parameterThis is a parametric equation There are six skills you need to know for parametric equationsVery often solving equations requires more than one step, but the method is still what you do to one side of the equation, you must also do to the other side Take for example 2 \({y}\) 6 = 12




Gcse Maths Revision Resources Maths Tuition And Science Tuition



How To Construct Equations Help With Igcse Gcse Maths Explainingmaths Com
Physics Equations and DfE Maths skills BOOKLET 1 Published date Summer 16 version 1 2 We have included all the parts of what good science is at GCSE level whether it be investigating, observing, experimenting or testing out ideas Explain why data is needed to answer scientific questions, and why it may be uncertain,These grades are the stepping stone to your future Even if you don't want to studY=mxc is a linear equation The term linear is used to describe a straight line and we can determine this because the power of x is equal to 1 If the power of x was equal to 2 (x 2) we would have a quadratic If the power of x was equal to 3 (x 3) we would have a cubic equation, and so on For now we are just going to look at linear equations of the form y=mxc




Gcse Maths Revision Resources Gcse Maths Revision Gcse Math Math Methods
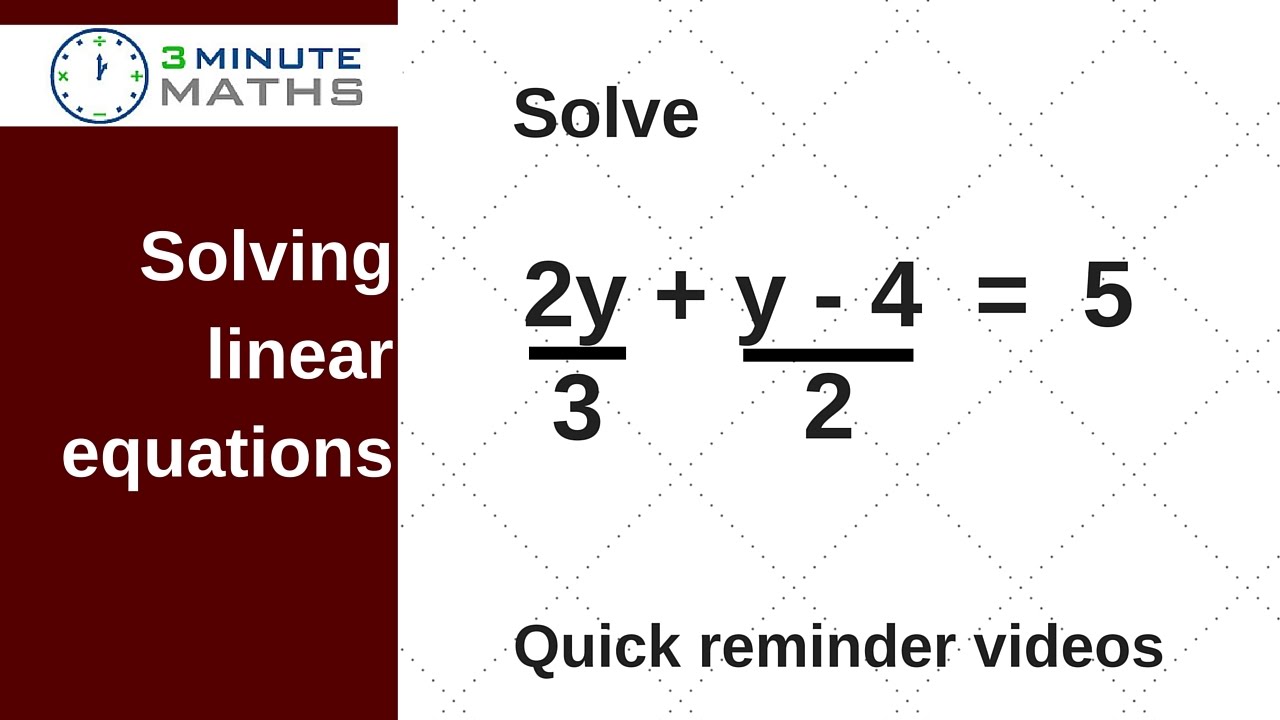



Linear Equations With Fractions Gcse Maths Level 7
Test your skills in using and rearranging formulae in this GCSE Maths quiz You have to know how to SUBSTITUTE a value into a formula – you do this when you are told what value a variable has Every time the letter appears in the formula, replace it with the number, remembering to keep the same relationships such as multiplying or addingSolving an equation means finding the value or values for which the two expressions on each side of the equals sign are equal One of the most common methods used to solve equations A doublesided poster of the formulae that your GCSE maths students need to know Creative Commons "Sharealike" Reviews 49 Something went wrong, please try again later matthew_mamvura_nia 2 years ago report 5 Empty reply does




Gcse Maths Revision Notes Past Papers And Cheat Sheet Resources Studying Revision Student Hacks



Maths Gcse 101 Exam Boards Mark Schemes Key Dates And Everything Else You Need To Know
;= 2 2− 2 2 Compound Measures Speed = Density = Pressure = Algebra The Quadratic equation =Since the 91 GCSE Maths course came into effect a few years ago, the need to memorise more equations has become apparent The exams no longer provide a formula sheet at the start but students are given the odd equation as and when they need it, but there is now the requirement to memorise more of them including the quadratic formula!Solving Linear Equations Linear equations are a type of equation that appear all over the place in maths They can look quite simple, like x2=5 or they can look a little more complicated There are 5 key types of linear equation you will need to solve Exam questions can contain multiple types to make it even harder




Quadratic Equations Mathematics Gcse Revision



Gcse Maths Revision Solving Linear Equations 1 Youtube On Vimeo
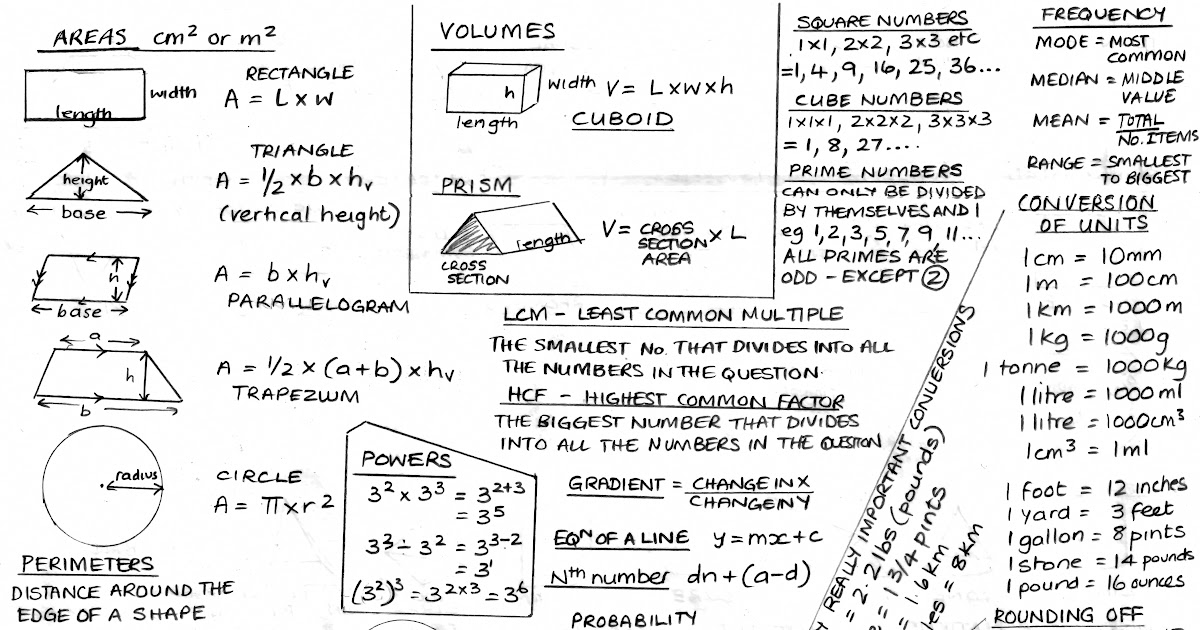
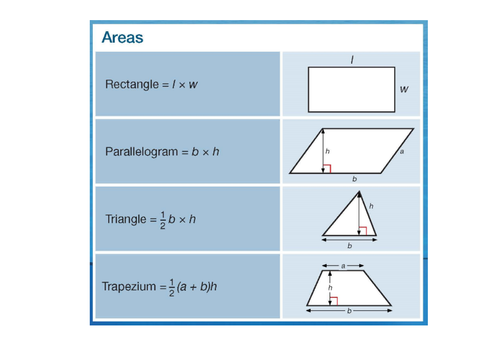
GCSE (9 1) Edexcel Maths Useful Formulae to Learn Subject Mathematics Age range 57 Resource type Visual aid/Display 5 6 reviews Miss Aslam's Resources 111 reviews Last updatedE1 Area of a rectangle A=L×W E2 Volume of a cuboid VTo work out the internal area of a shape, you will need to take into consideration the lengths of the sides of the shape A = Area of the shape Rectangle = A = length x width Parallelogram = A = base x height Triangle = A = ½ base x height Trapezium = ½ (ab)h Circles
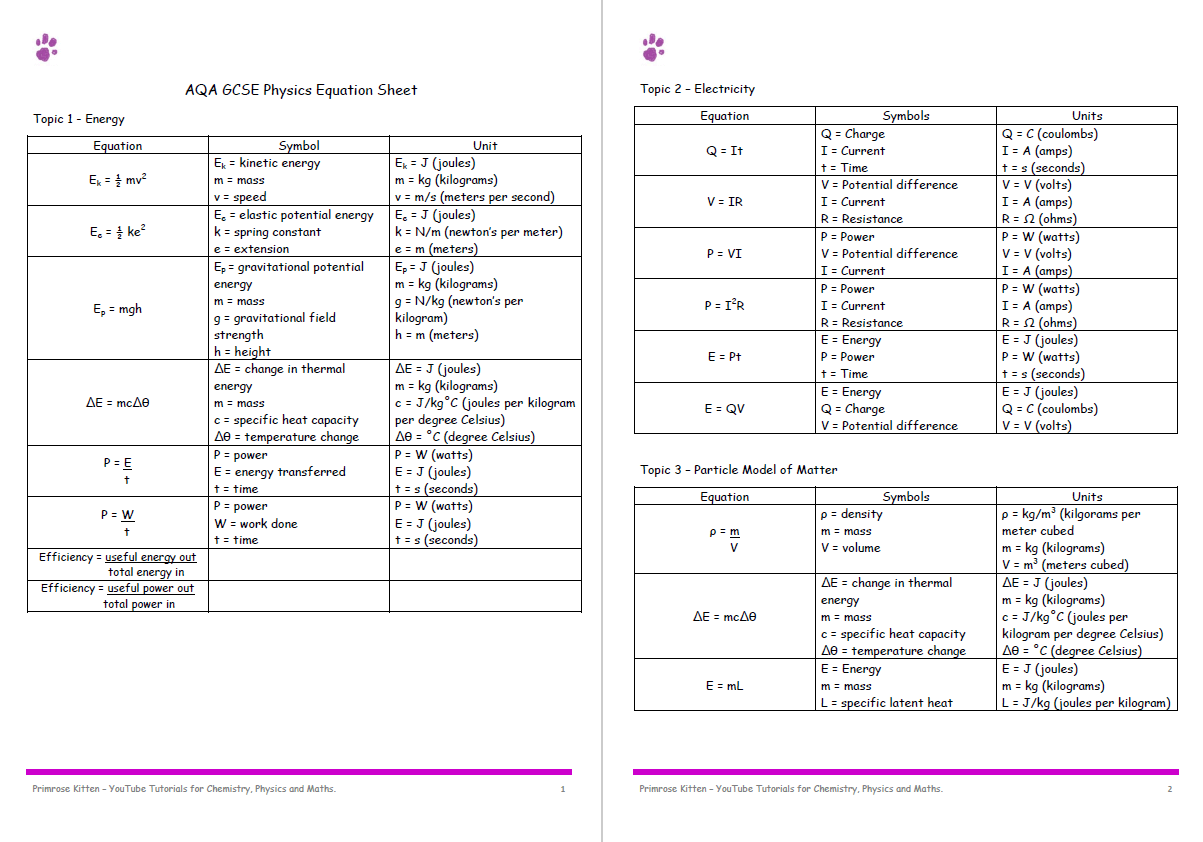



7 Of The Best Gcse Physics Equation Sheets And Revision Resources




Welcome Gcse Maths Ppt Download
GCSE Maths Higher Formula Sheet These formulae are not given to you and you need to know them St Anthony's Girls' Catholic Academy = 2−1 2− 1 Gradient of a Line (x 1 , y 1) (x 2 , y 2) or = height base base t This can be incredibly useful for your GCSE Maths exams, as this is a skill that is commonly tested The secondbest option you have is the Casio FX85GT Plus This calculator is a safe pick for GCSE Maths, and is the probably the most common calculator people buy The last option is the Casio FXGTXCollect all x terms (or whatever you are solving for) onto one side of the brackets and move everything else to the other Remember if it is positive on one side then it becomes negative on the other Combine the x terms so the equation becomes "Ax = " Divide both sides by A so then the equation becomes "x = "




Gcse Maths Formula Sheet All Exam Boards Mme



Http Www St Anthonys Academy Com Wp Content Uploads 14 07 Gcse Formulae Sheet Foundation Pdf
GCSE Maths Revision Guide (with Online Edition) Higher This CGP textbook consists of topics divided into sections for easy digestion Covering numbers, graphs, algebra and geometry and measures, this useful resource tackles all of those tricky lessons that many students needI've searched google so much but cant find an actual list of ALL the equations i NEED to know Hey, I'm doing my Alevels now so I've kind of forgotten which ones they exactly are, but you should try Quizlet it should help xShow 10 more gcse physics
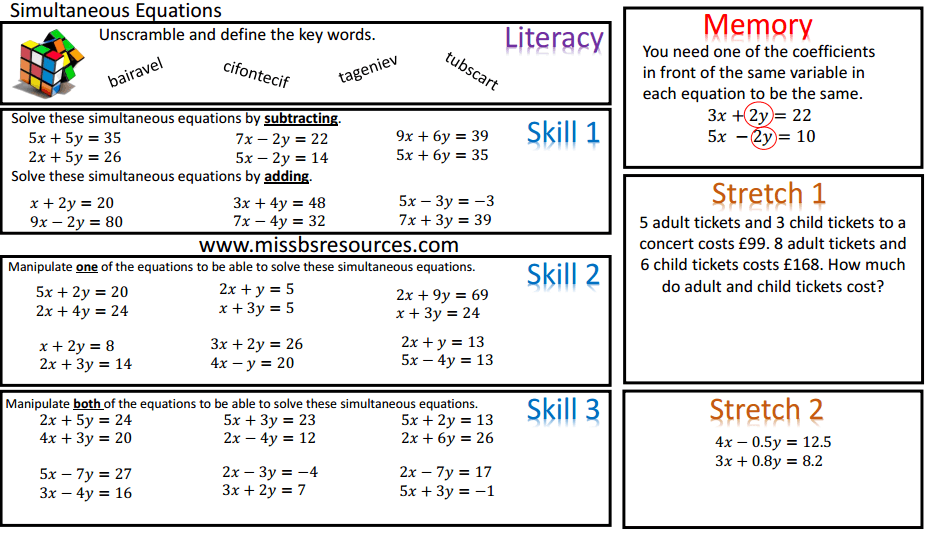



Algebra



Diagnositc Questions Gcse Maths Exam Papers Mr Barton Maths Blog
What equations must i need to know for AQA higher Chemistry? This equation (which you know from Maths) will be necessary when analysing inhibition zones caused by antibiotics or antiseptics on bacterial growth Pi (π) can be estimated at 314 and r is the radius of a circle (half the diameter) Area of a circle = π r 2 Calculating the rate of reactionExam Formula Sheets The formula sheets given to you in the GCSE Maths exams are below Each exam board's formula sheet is very similar




3 8 1 Equations Problem Solving




Aqa Gcse Physics Equations Formulae Teaching Resources Gcse Physics Gcse Science Gcse Physics Revision
How to solve equations In order to solve equations, we need to work out the value of the unknown variable by adding, subtracting, multiplying or dividing both sides of the equation by the same value In GCSE Maths there are two main types of equations that we need to solve, both of which are covered belowThere is a formula for completing the square (X b/2)^2 C (b/2)^2 Most students won't memorise any formula for completing the square so it won't be listed in eg the page I linked to above 0 reply X start new discussion Page 1 of 1 Go to first unread• Students will be required to memorise formulae – fewer formulae will be provided in examinations Together these changes are designed to help students emerge from GCSE Maths with a level of confidence and fluency that will provide a genuine foundation for the rest of their learning and working lives 4 5 Find all our support on www
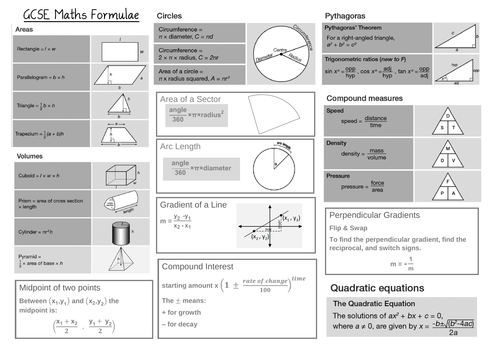



Gcse 9 1 Edexcel Maths Useful Formulae To Learn Teaching Resources




Formula Students Need For Gcse Maths 9 1 Teaching Resources
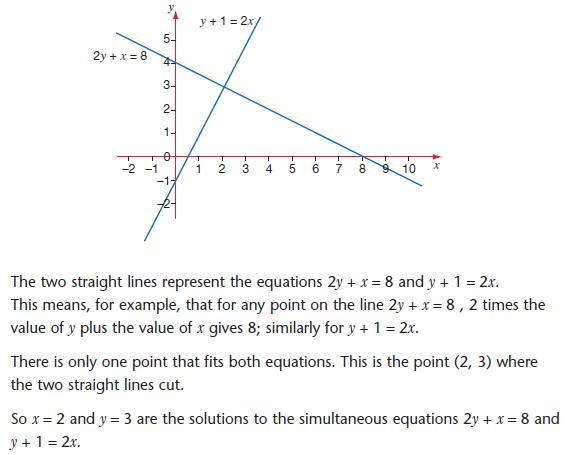
The general example of a quadratic equation is written as ax2bxc= 0 a x 2 b x c = 0 a is coefficient (number in front) of the x 2 term b is coefficient (number in front) of the x term c is the constant term (number on its own) At GCSE the solutions to polynomial equations such as quadratics will always give real numbers but they canX y = 25 We cannot say what x and y are in the equation above because there are an infinite number of possibilities x = 1, y = 24 x = 21, y = 4 etc In general, a single equation with two unknowns (we don't know x and y in this case) cannot be solved What we need is a second equation involving at least one of the unknown variablesDoes Foundation Tier Math Books cover Key Stage 1, 2 and 3?




Simultaneous Equations Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme




1 Of 66 Gcse Maths Starter 3 1 What Is 2 3 Of 210 2 Solve The Equation To Find X 4 X 5 44 3 What Is The Probability Of Throwing A 4 On An Ordinary Ppt Download
To understand this, you need to first understand the Algebra Basics Easy Example This one is easier as both of the equations are linear (they have so powers) Example – Solve the simultaneous equations 3x – 2y = 11 x 3y = 11 First label the equations so you can keep track and explain to the examiner what you are doingThe Cosine rule 2= 2 2 ;−2 cos ;




Pa Gcse Maths A P2 1ma0 2h Jun15 07 08 152 Pa0228 Gcse Mathematics 1ma0 Formulae Higher Tier You Must Not Write On This Formulae Page Anything You Write On




Area Formulae Edexcel Igcse Maths Revision Notes



1




Edexcel Formulae For New Maths 9 1 Gcse You Need To Know These Youtube




Tutor2u Maths Grab Your Free Classroom Posters On The Formulae Needed For Gcse 9 1 This Summer T Co Xwcoormtht Gcsemaths Mathsteacher T Co Yy0ndrkkxi



Formula Sheet Maths Gcse Edexcel Math Formulas



Maths Gcse 1 9 Edexcel Formula Need To Know Teaching Resources




Smarter Revision Cards Book Gcse Maths 9 1 Higher Aqa Amazon Co Uk Redcliffe Valerie Redcliffe Philip Books




Maths Gcse Exam Revision Equation Of A Circle Ezyeducation



Www Southwigston Leics Sch Uk Documents 1029 Gcse Mat Higher2 Pdf




Forming Solving Simultaneous Equations Go Teach Maths Handcrafted Resources For Maths Teachers
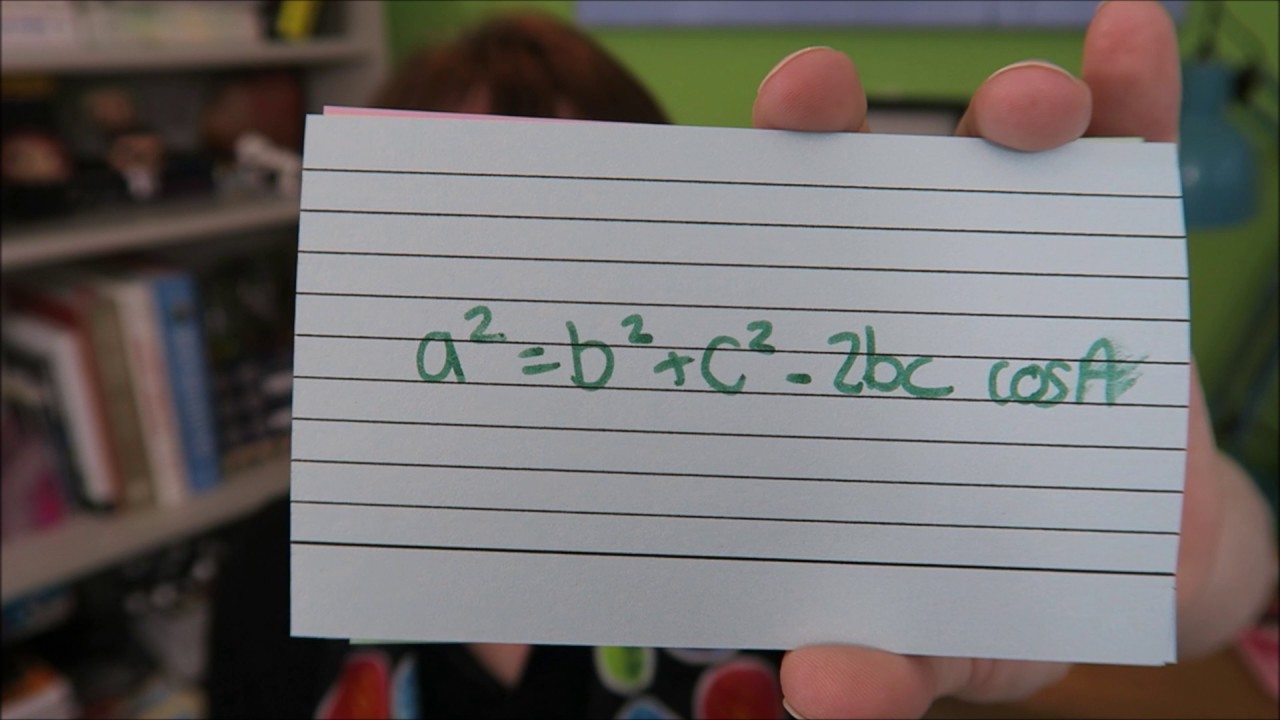



Must Learn Formulae For Gcse Maths Edexcel Higher Youtube



How To Revise For Gcse Maths Quizlet



Exam Formula Sheets Revision Maths



Http Www Thechalkface Net Resources Gcse Maths Formulae Pdf



Simultaneous Linear Equations Gcse Revision Maths Number And Algebra Algebra Simultaneous Linear Equations Revision World




Rearranging Formulae Poster Math Poster Gcse Math Gcse Maths Revision




Equations And Formula Must Learn For Gcse Maths Revision For Aqa Edexcel Eduqas Wjec Or Ocr Youtube



Http Www St Anthonys Academy Com Wp Content Uploads 14 07 Gcse Formulae Sheet Foundation Pdf




Gcse Maths Formula To Learn Aqa Math Formulas




100 Proof The Why Of Maths Visual And Algebraic Explanations Of Formulas Needed For Gcse And A Level Mathematics Visual And Algebraic Explanations Needed For Gcse And A Level Mathemetics Amazon Co Uk




Quadratic Equations Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet




Gcse Revision Checklists Gcse Math Studying Math Gcse In 21 Studying Math Gcse Math Math Methods




Equation Of A Line Practice Questions Corbettmaths




Gcse Algebra 1 Enotes Solving Linear Equations Word Problems Notes Maths Gcse Irevise



Exam Formula Sheets Revision Maths




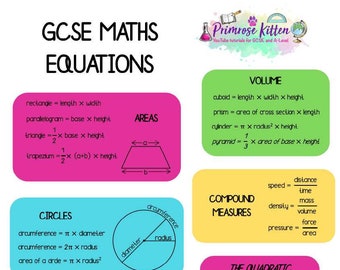
Gcse Maths Equation Poster Primrose Kitten




Simultaneous Equations Gcse Maths Revision Guide Tutor In
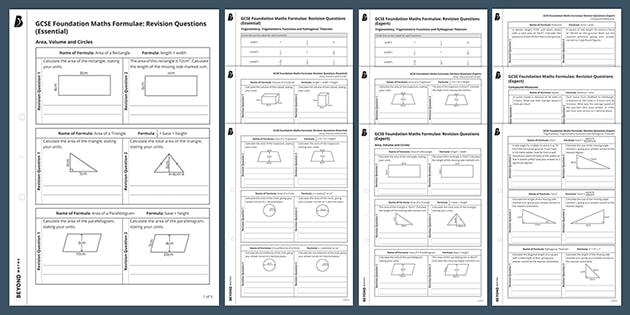



Gcse Foundation Maths Revision Questions Formulae
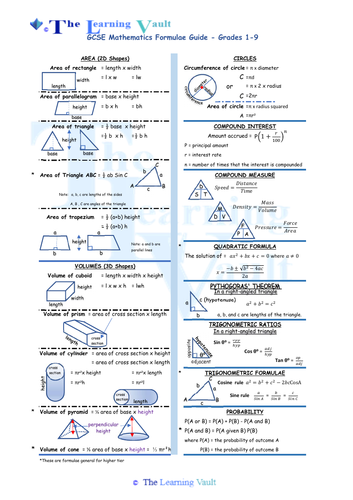



Gcse Mathematics Formulae Sheet Teaching Resources
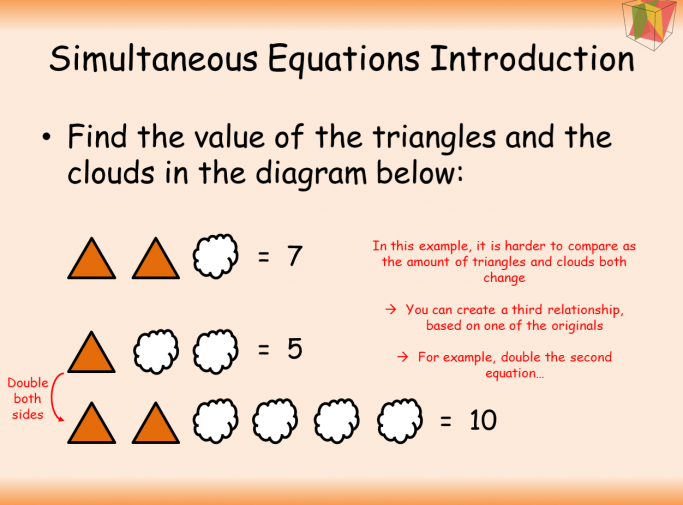



26 Free Simultaneous Equations Worksheets And Lesson Plans For Ks3 And Ks4 Maths




Simultaneous Equations 1 Gcse Higher Maths Tutorial 11 Youtube



Simultaneous Equations Revise Algebra Gcse Maths Tutor




Gcse Maths Problem Solving Questions Worbook Solving Quadratic Equations By Maths School
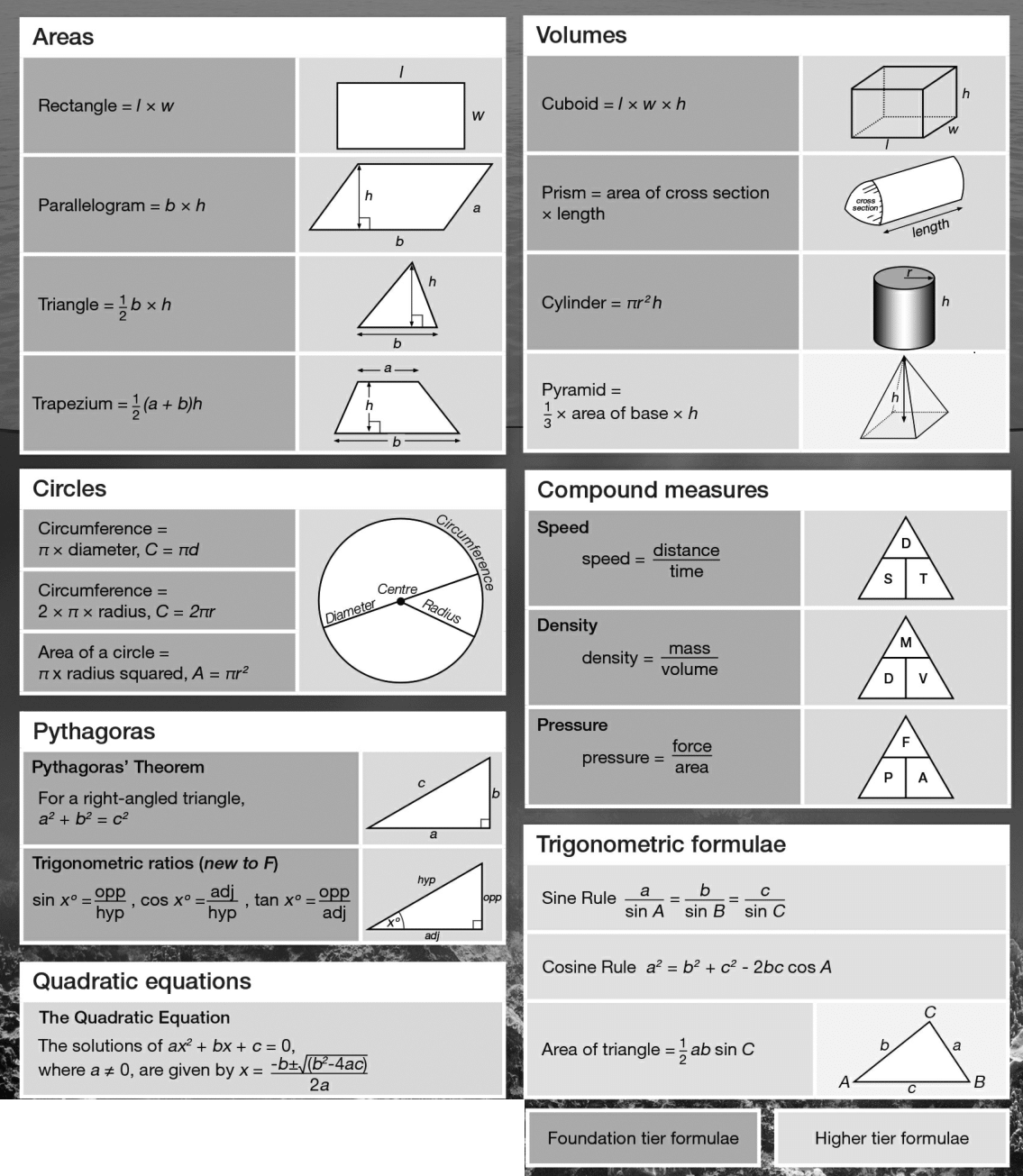



Gcse Maths Video Lessons Examples Solutions Worksheets Activities Games
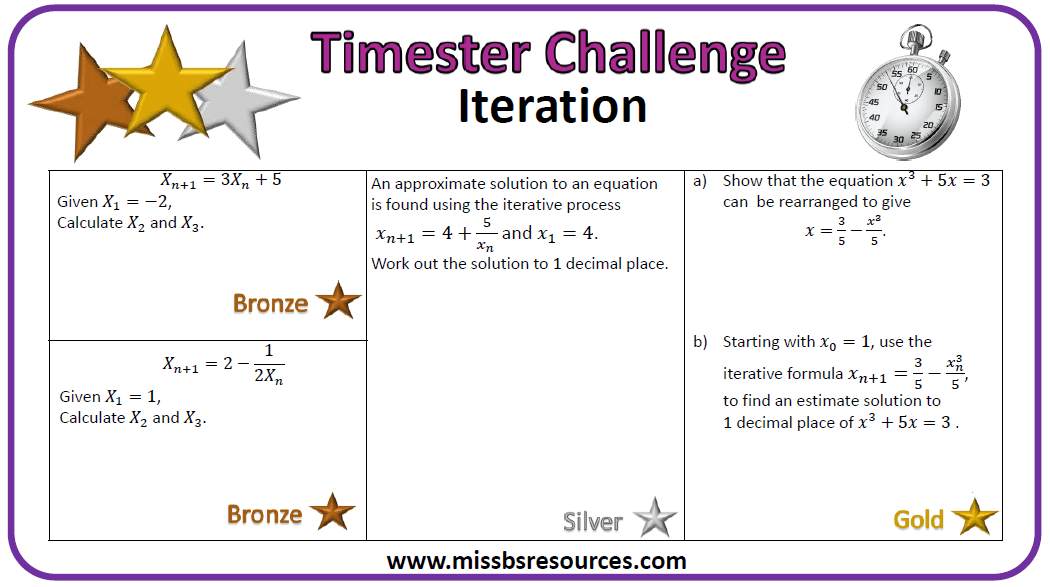



Algebra




Gcse Maths Preparing For Your Exam




Gcse Physics Equation Poster Primrose Kitten



1
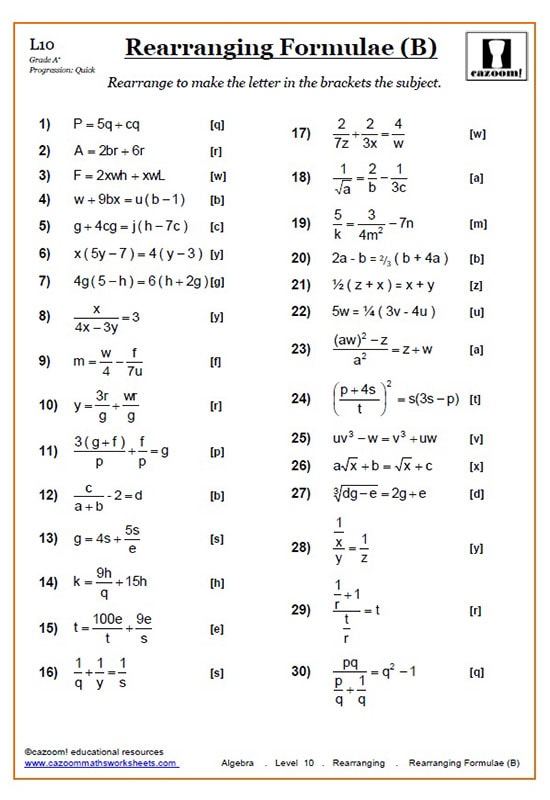



Rearranging Equations Worksheets Cazoom Maths



Revisionmaths Com Gcse Maths Revision Algebra Quadratic Equations




How To Remember Equations And Formulae For Gcse Maths Home Facebook
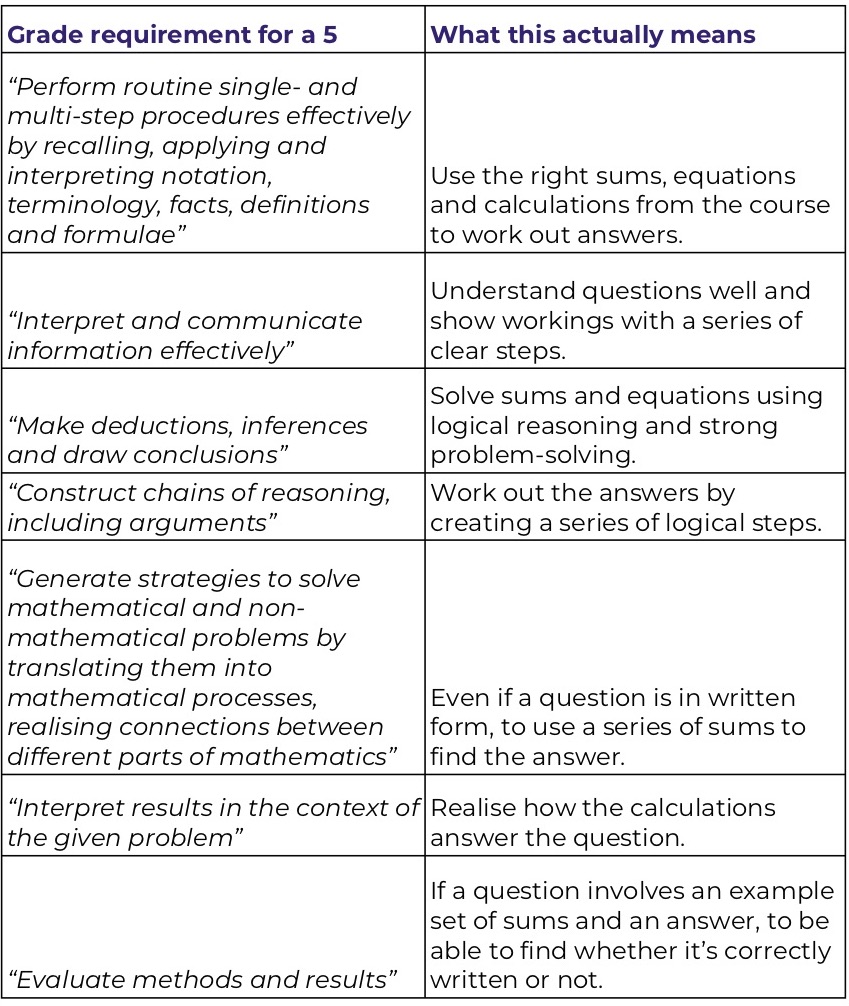



Maths Gcse 101 Exam Boards Mark Schemes Key Dates And Everything Else You Need To Know



Simple Equations Revise Algebra Gcse Maths Tutor



Http Www St Anthonys Academy Com Wp Content Uploads 14 07 Gcse Formulae Sheet Foundation Pdf
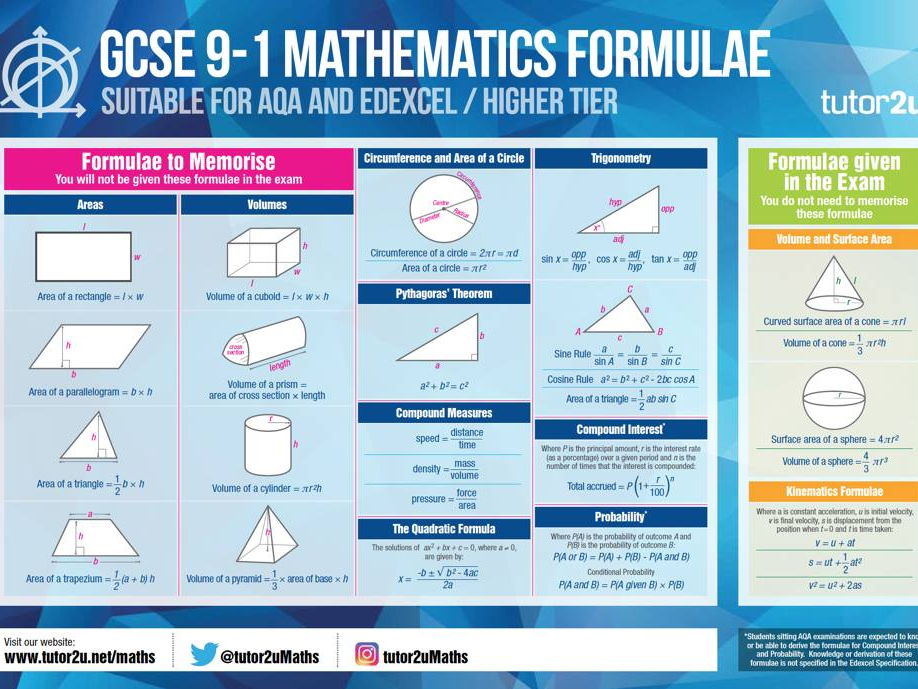



Gcse 9 1 Maths Formulae Classroom Posters And Free Orders For A1 Sized Versions Teaching Resources




Spice Of Lyfe Physics Equations Gcse Aqa Paper 1 Gcse Science Gcse Physics Gcse Physics Revision
/Quadratic-Equations-(H).jpg)



Gcse Quadratic Equations Solving Unknown Quantities



1




Gcse Maths Mechanics Vertical Motion How To Apply Suvat Equations To Solve Problems Homeworkhelp




Gcse Maths Explained How Does The Non Calculator Test Work And What Equations Do I Need For The Exam



Math Equation Etsy




Gcse Maths Formulae For The New 9 1 Grade Exams You Will Have To Learn All Of These Gcse Math Maths Exam Igcse Maths




Gcse Maths Equations Formulae To Learn Mme



Gcse Maths Questions By Topic Foundation And Higher
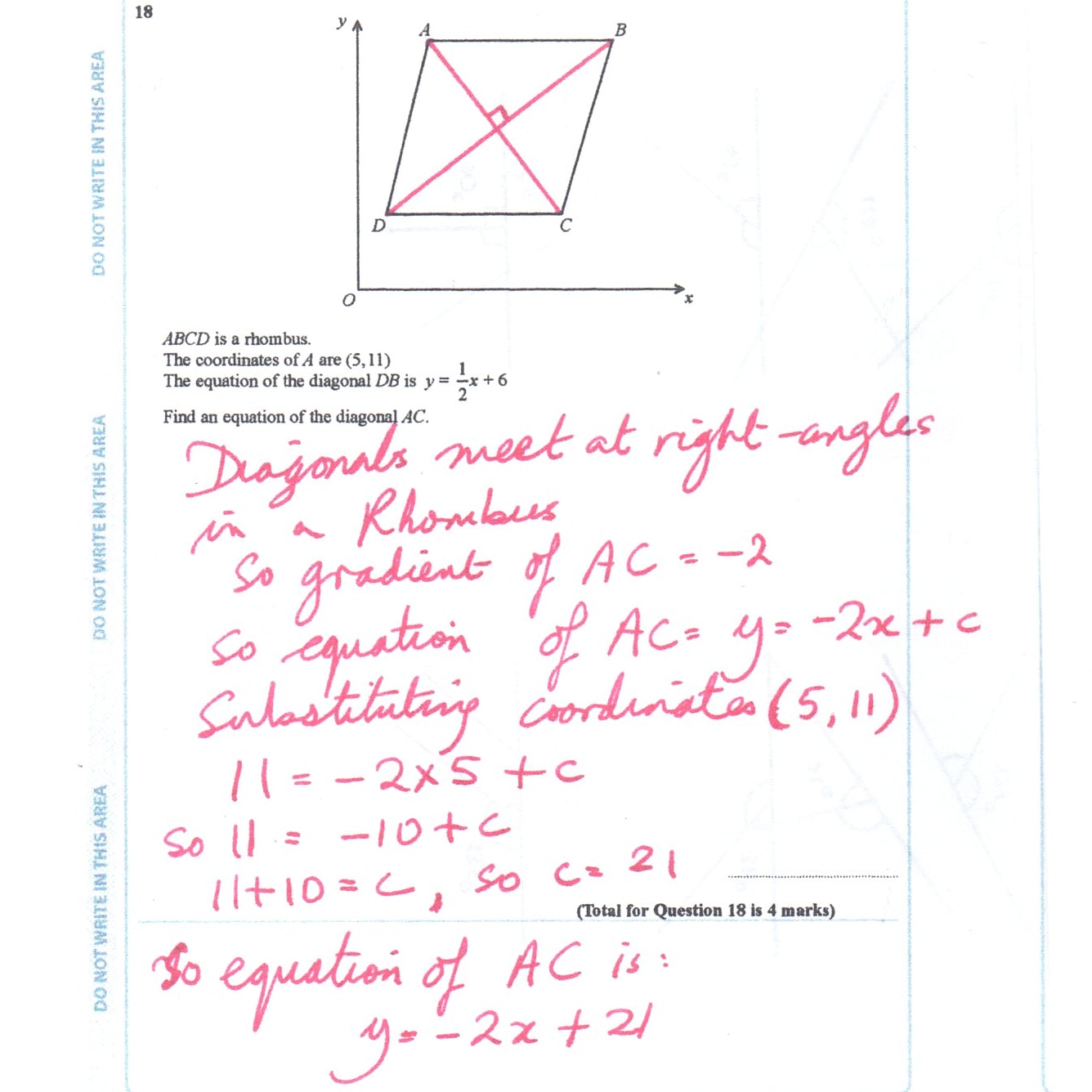



Arithmatix Edexcel Gcse Maths Higher Practice Paper Question On Equations Of Lines Edexcelmaths Math Gcse Linegraph Linegraphs Gradients Rhombus Perpendicular Diagonals Equal Test Testing T Co Pxobfwtnie
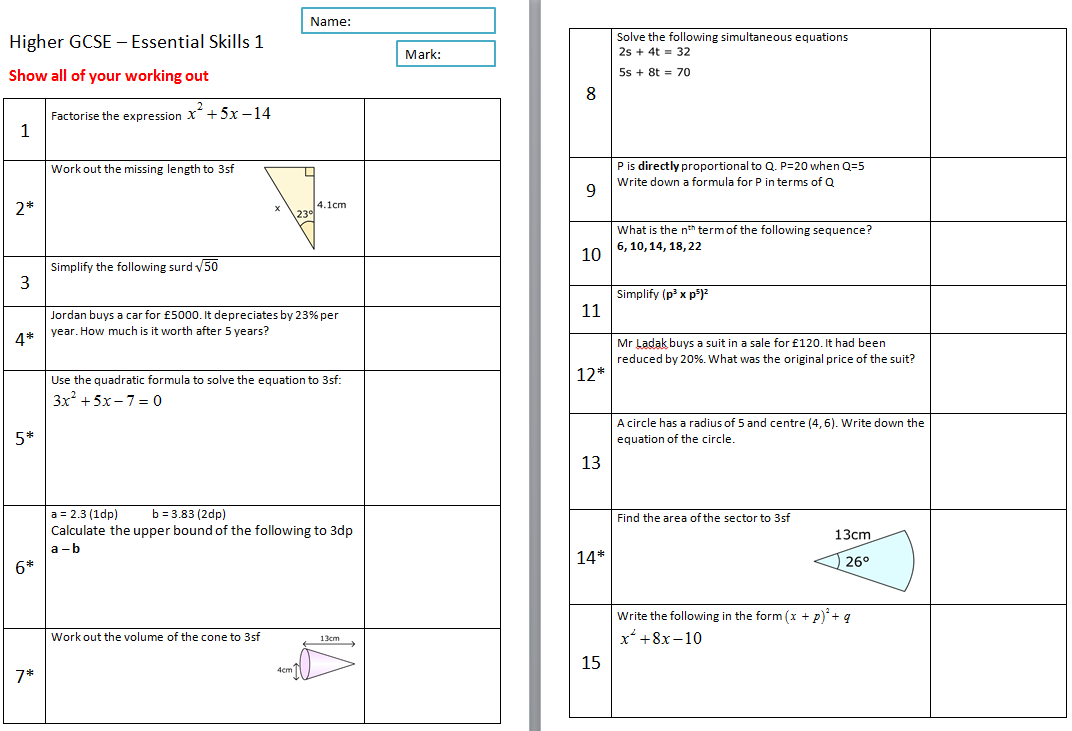



Essential Skills Higher Gcse Mathedup
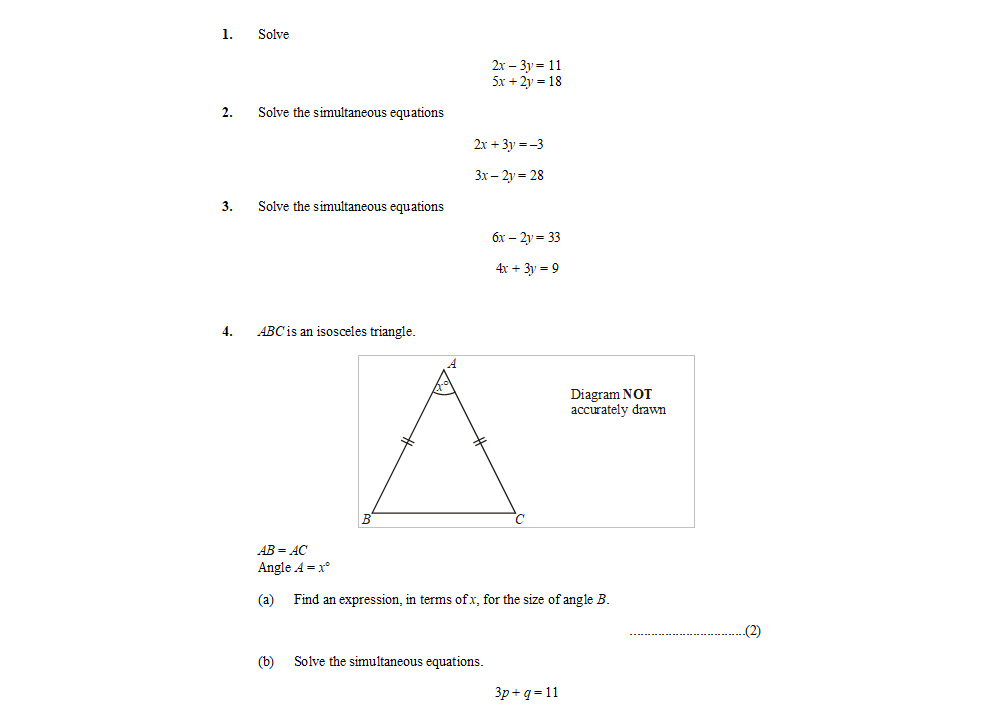



Simultaneous Equations Worksheets For Gcse Maths Teachwire Teaching Resource
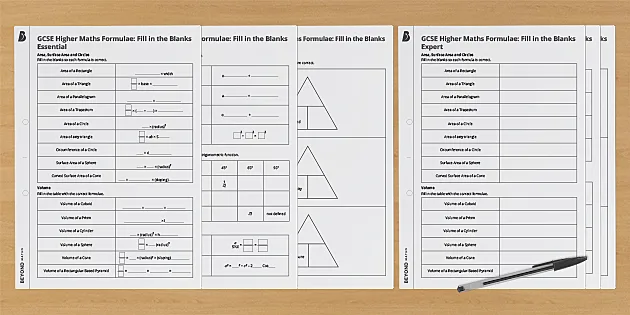



Gcse Higher Maths Formulae Activity Ks4 Maths Beyond
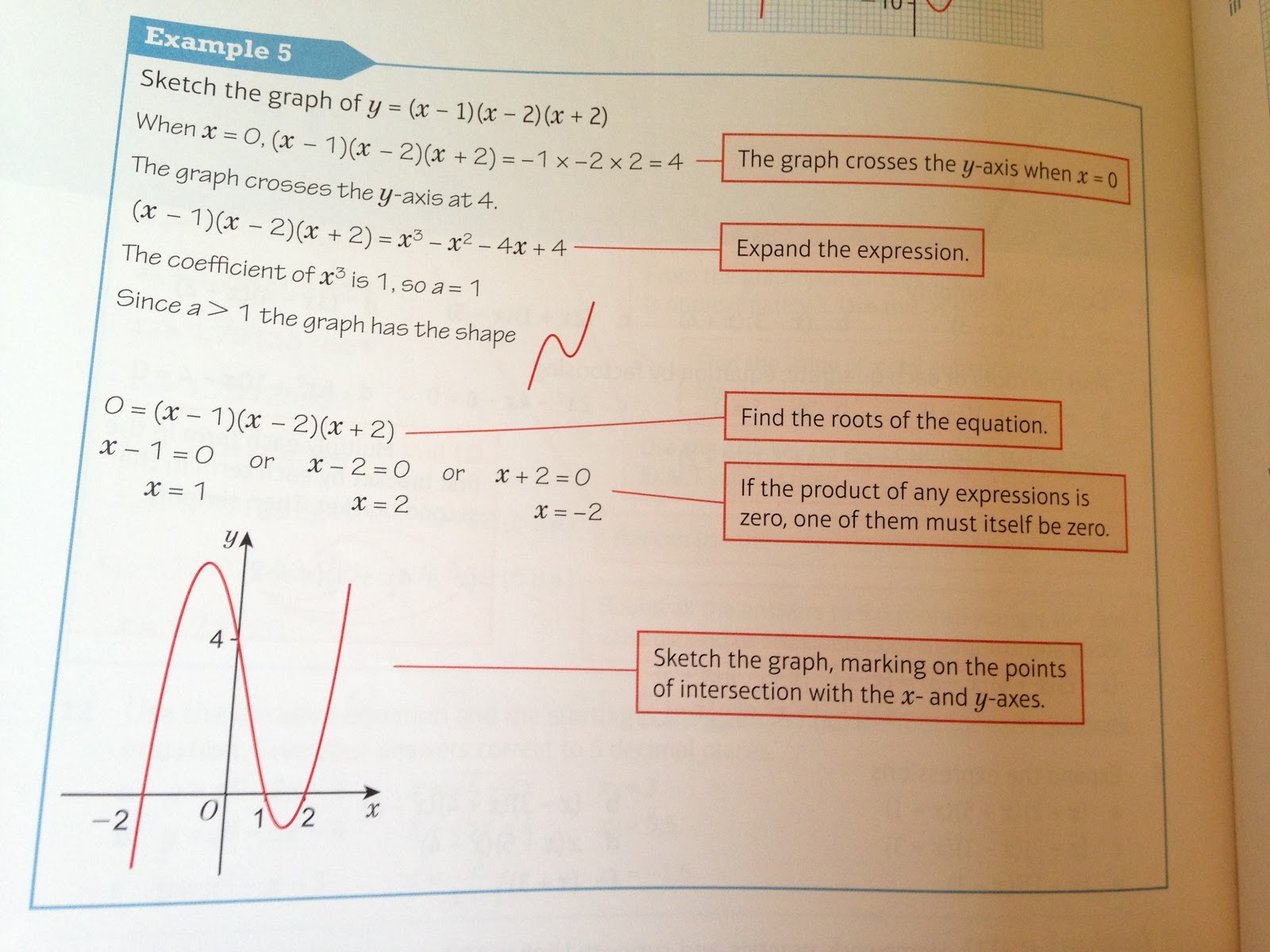



Resourceaholic Five Things You Might Not Know About The New Gcse Content 2




How To Do Forming Expressions Equations C To A Gcse Higher Maths Exam Revision Practice Help Youtube



Www Rvhs Co Uk S W148 Gcse Maths Poster Pdf
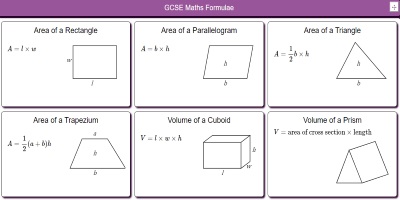



Mathsbot Com Tools For Maths Teachers
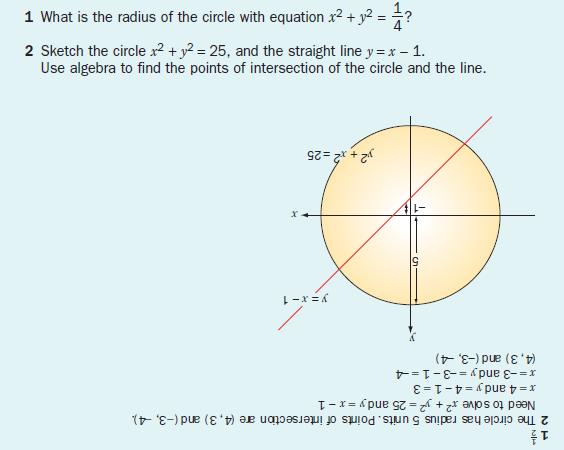



Circles And Equations Gcse Revision Maths Number And Algebra Algebra Circles And Equations Revision World




Gcse Maths 9 1 Formulas Revision Poster Teaching Resources




Simultaneous Equations Worksheet
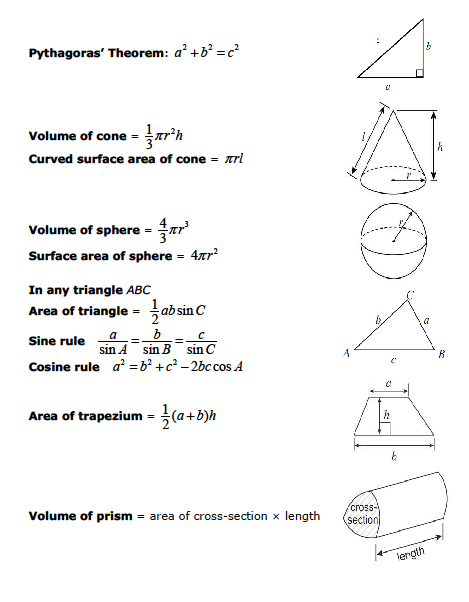



Exam Formula Sheets Revision Maths



Www St Anthonys Academy Com Wp Content Uploads 14 07 Gcse Formulae Sheet Higher Pdf




Vamsiz Vamsimahanti Profile Pinterest




Simultaneous Equations Practice Questions Gcse Maths Tutor In




Videos Maths Tutor2u




Ks4 Gcse Maths Formulae Sheets For Higher Foundation Teaching Resources



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿